We’ve all known a “natural”. Be it academics, sports or what-have-you, we’re talking about that person who is naturally wired for a task. Who just…”gets it”. Then there is a second type. One born without that natural talent whose success depends on guts, drive and determination to succeed.
When it came to sports, Terrance Stanley Fox was one of those.
The second child of four born to Betty and Rolland Fox, Terry arrived on July 28, 1958 in Winnipeg, Manitoba, the family later moving to British Columbia, the westernmost province in Canada.
Terry’s best buddy Doug Alward was a basketball natural, starting for the Mary Hill Jr. High School Cobras. Fox loved the sport but basketball is difficult for a guy who stood barely five feet high in Jr. high. Coach Bob McGill suggested he go out for cross country which he did, but he never lost the desire to play hoops.

Fox would practice every morning before school and during the summers. He finally made the team in grade 8, dead last, and only played a single minute for the whole season. By grade 10 Fox and Alward were first string guards for the Port Coquitlam High School Ravens. Later that year the two shared the school’s Athlete of the Year award. Fox continued with cross-country running and also soccer and rugby. By grade 12 Fox was actually the better basketball player while Alward went on to distinguish himself, in long distance running.
The year was 1976. The year when Terry first noticed that pain, in his right leg.
Terry began college that year at Simon Fraser University where he tried out and won, a place on the schools Junior Varsity basketball squad. A car wreck later that year did little to help that sore knee. Terry worked through it but, a training run the following spring left him in so much pain he could barely move. Suspecting something more serious Rolly took his son to the family doctor.
Dr. Michael Piper suspected osteogenic sarcoma, an aggressive bone cancer which often begins in the knee. The diagnosis was confirmed on March 4. The only choice was amputation.
The night before his surgery, high school basketball coach Terri Fleming brought him an article. It was about an amputee named Dick Traum who went on to run the marathon, in New York city. “Someday” he told nurse Judith Ray the following morning, “I’m going to do something like that”. Doctors amputated the leg above the knee on March 9, 1977.
Terry was walking again in a few weeks, with the help of an artificial leg. There were chemotherapy sessions and physiotherapy. Golf dates with his father and through it all, a growing sense of…something. Yes his hair was falling out but Terry saw other cancer patients during this time and somehow, he felt like one of the lucky ones. Many of these people were destroyed by this disease, some were dying, but…Terry…he had a Future.
There were sixteen months of chemotherapy and, despite the nausea, Terry took up wheelchair basketball. His hands would blister and bleed as he struggled to master this new approach to an old game. Within two years he had made the national team.

But he never forgot that article, or his own sense of responsibility to those who, like himself, suffered from this terrible disease.
Fox began to train at night, first a half-mile, and then more. Prosthetist Ben Spencer helped with modifications to his artificial leg, making it easier to withstand the impact of running.
There was a half-marathon in 1979 in which he finished dead last but only ten minutes behind, the last two-legged runner. Around this time Terry had an idea that turned into an obsession. A fund raiser for cancer research. He would run across Canada in a “Marathon of Hope” and he would do it, the following spring. The goal to raise $24 million, representing a dollar from every person in Canada.
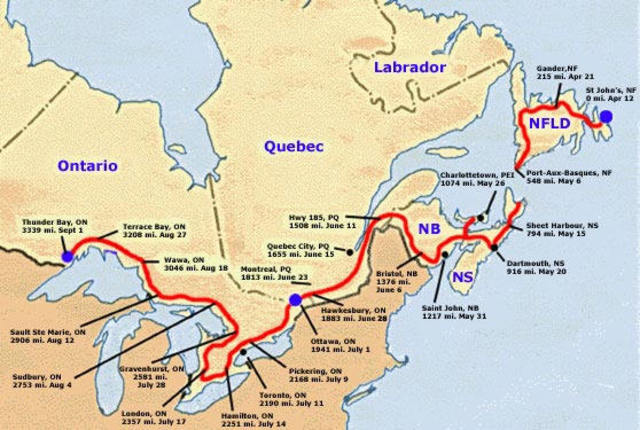
The marathon of hope got off to a wet, cold start on April 12, 1980, when Terry dipped his artificial leg in Atlantic waters, off of Newfoundland. He filled two bottles, one for a souvenir and the other, he would dump into the Pacific.
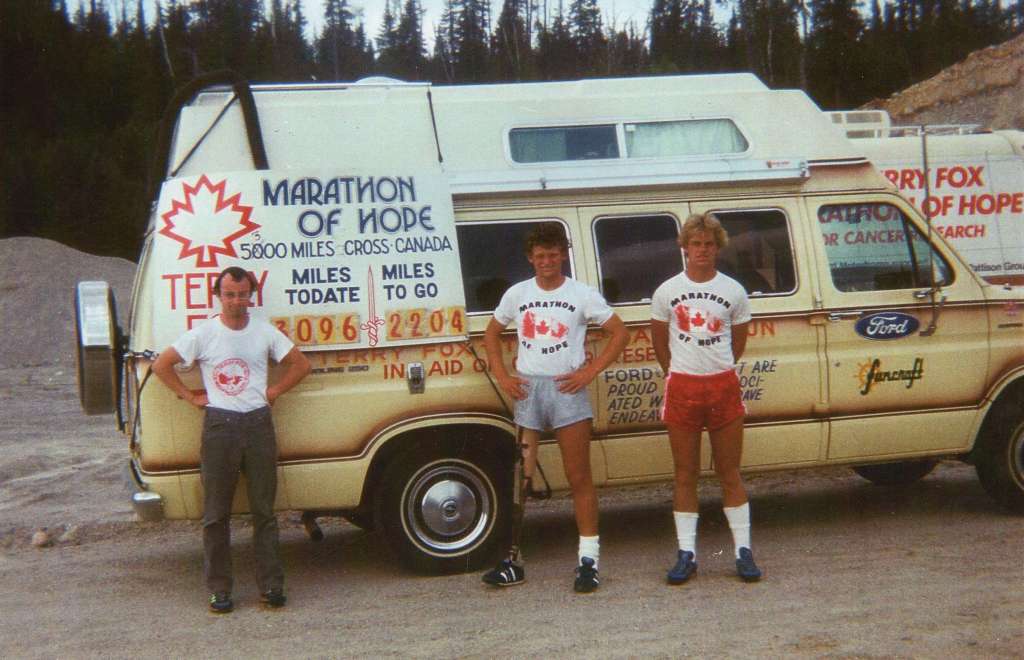

The response was disappointing throughout much of the maritime provinces. Little had been done to publicize the run. Very few even knew it was happening. Terry pushed on running about 42km a day, supported by Doug Alward in the van and later joined by Terry’s brother, Darrell.
Nothing whatever had been done to publicize the run throughout all of Quebec but that all changed in Ontario, with the help of businessman Isadore Sharp and Bill Vigars, of the Canadian Cancer Society. Journalist Leslie Scrivener of the Toronto Star began to write a weekly column on Fox’s run.
He became a national star in Ontario, gaining personal meetings with Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau, British actress Maggie Smith and NHL Greats Darryl Sittler and Bobby Orr.
For 143 days Fox ran ever westward covering a total of 5,373 kilometers, equivalent to over 128 full-length marathons. It all came to an end on September 1 in a place called Thunder bay.
The pain he could live with. Terry Fox had demonstrated that but the cough was relentless, and debilitating. The cancer had returned and now, it was in his lungs. He was airlifted on September 2.
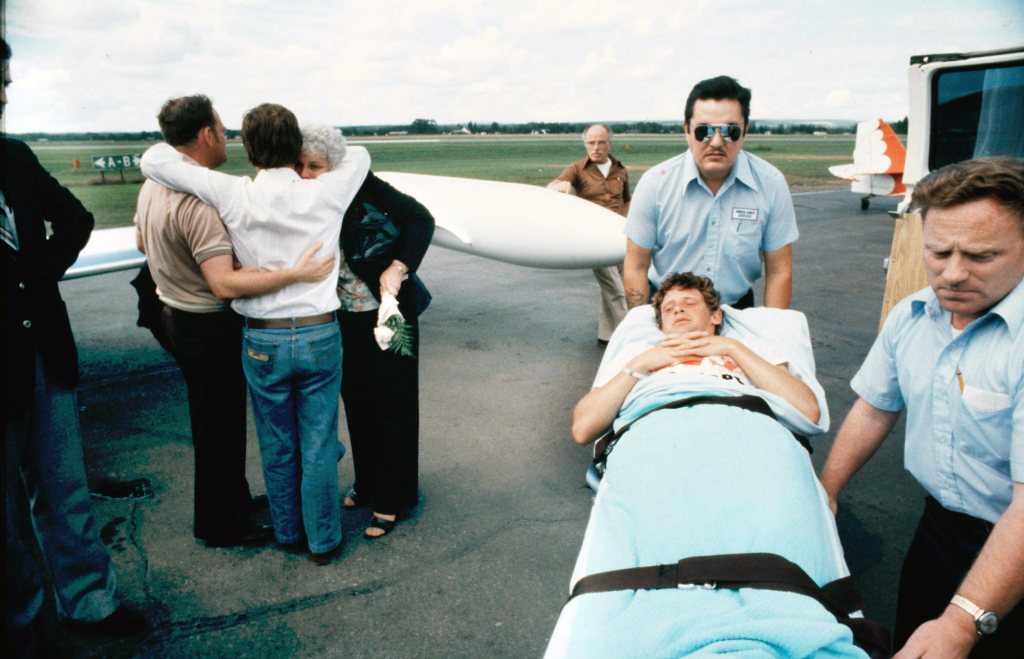
The CTV telethon airing later that week raised $6.5 million, for cancer research. Fox received the Companion to the Order of Canada two weeks later, becoming the youngest person ever to win Canada’s highest civilian honor. That December he won the Lou Marsh trophy as Canada’s Athlete of the Year.
Port Coquitlam High School was later renamed, in his honor.
Donations topped $24.17 million on February 1, 1981, achieving Terry’s goal of raising a dollar from every person in Canada. Terry Fox’s Marathon of Hope was a success. His struggle against that hideous disease which had taken his leg, was not.
There were long months of cancer treatments but this thing was relentless. In June 1981 Terry contracted pneumonia. He went into a coma on June 27. Terry Fox died at 4:35 am on June 28 at Royal Columbian Hospital. He would have been 23 in about a month.
Flags across all of Canada were lowered that day, to half-staff. Let Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau have the last word in this story as he himself spoke, before the House of Commons:
“It occurs very rarely in the life of a nation that the courageous spirit of one person unites all people in the celebration of his life and in the mourning of his death. Our profound gratitude for the gift which Terry gave to all of us, the gift of his own boundless courage and hope.”























































You must be logged in to post a comment.