 It was D+4 in the invasion of Normandy, and the 2nd SS Panzer Division (“Das Reich”) had been ordered to stop the Allied advance. They were passing through the Limousin region in west central France, when SS-Sturmbannführer Adolf Diekmann received word that Waffen-SS officer Helmut Kämpfe was being held by French Resistance forces in the village of Oradour-sur-Vayres.
It was D+4 in the invasion of Normandy, and the 2nd SS Panzer Division (“Das Reich”) had been ordered to stop the Allied advance. They were passing through the Limousin region in west central France, when SS-Sturmbannführer Adolf Diekmann received word that Waffen-SS officer Helmut Kämpfe was being held by French Resistance forces in the village of Oradour-sur-Vayres.
Diekmann’s battalion sealed off the nearby village of Oradour-sur-Glane, unaware that they had confused it with the other village. Everyone in the town was ordered to assemble in the village square to have their identity papers examined. The entire population of the village was there, plus another 6 unfortunates who were riding their bicycles in the wrong place, at the wrong time.

The women and children were locked in a village church while German soldiers looted the town. The men were taken to a nearby barn, where machine guns had already been set up.
The Germans aimed for the legs when they opened fire, intending to inflict as much pain as possible. Five escaped in the confusion before the SS lit the barn on fire. 190 men were burned alive.
Nazi soldiers then lit an incendiary device in the church, and gunned down 247 women and 205 children as they tried to get out.
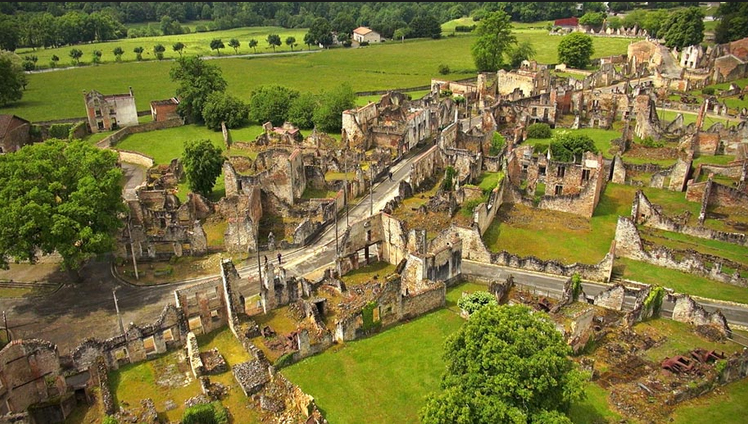
642 inhabitants of Oradour-sur-Glane, age one week to 90 years, were murdered in a few hours, the village razed to the ground. After the war, French President Charles de Gaulle ordered that the village remain as is; a memorial to the cruelty of collective punishment, and the savagery committed by the Waffen-SS in countless places: the French towns of Tulle, Ascq, Maillé, Robert-Espagne, and Clermont-en-Argonne; the Polish villages Michniów, Wanaty and Krasowo-Częstki, Warsaw; the Soviet village of Kortelisy; the Lithuanian village of Pirčiupiai; the Czechoslovakian villages of Ležáky and Lidice; the Greek towns of Kalavryta and Distomo; the Dutch town of Putten; the Yugoslavian towns of Kragujevac and Kraljevo, and the village of Dražgoše, in what is now Slovenia; the Norwegian village of Telavåg; the Italian villages of Sant’Anna di Stazzema and Marzabotto. And on, and on, and on.
French President Jacques Chirac dedicated a memorial museum in 1999, the “Centre de la mémoire d’Oradour”. The village stands today as the Nazis left it, 73 years ago today. It may be the most forlorn place on earth.
The story was featured in the 1974 British television series “The World at War”, narrated by Sir Laurence Olivier. The first and final episodes of the program began with these words: “Down this road, on a summer day in 1944. . . The soldiers came. Nobody lives here now. They stayed only a few hours. When they had gone, the community which had lived for a thousand years. . . was dead. This is Oradour-sur-Glane, in France. The day the soldiers came, the people were gathered together. The men were taken to garages and barns, the women and children were led down this road . . . and they were driven. . . into this church. Here, they heard the firing as their men were shot. Then. . . they were killed too. A few weeks later, many of those who had done the killing were themselves dead, in battle. They never rebuilt Oradour. Its ruins are a memorial. Its martyrdom stands for thousands upon thousands of other martyrdoms in Poland, in Russia, in Burma, in China, in a World at War”.











 Several measures were taken in the 1760’s to collect these revenues. In one 12-month period, Parliament passed the Stamp Act, the Quartering Act, and the Declaratory Act, and deputized the Royal Navy’s Sea Officers to help enforce customs laws in colonial ports.
Several measures were taken in the 1760’s to collect these revenues. In one 12-month period, Parliament passed the Stamp Act, the Quartering Act, and the Declaratory Act, and deputized the Royal Navy’s Sea Officers to help enforce customs laws in colonial ports.
 A few days later, a visiting minister in Boston, John Allen, used the Gaspée incident in a 2nd Baptist Church sermon. His sermon was printed seven times in four colonial cities, one of the most widely read pamphlets in Colonial British America.
A few days later, a visiting minister in Boston, John Allen, used the Gaspée incident in a 2nd Baptist Church sermon. His sermon was printed seven times in four colonial cities, one of the most widely read pamphlets in Colonial British America.


 Any question you had as to their purpose would have been immediately answered, as these strangers sprinted up the beach and chased down everyone in sight. These they murdered with axe or spear, or dragged them down to the ocean and drowned them. Most of the island’s inhabitants were dead when it was over, or taken off to the ships to be sold into slavery. All of those precious objects were bagged, and tossed into the boats.
Any question you had as to their purpose would have been immediately answered, as these strangers sprinted up the beach and chased down everyone in sight. These they murdered with axe or spear, or dragged them down to the ocean and drowned them. Most of the island’s inhabitants were dead when it was over, or taken off to the ships to be sold into slavery. All of those precious objects were bagged, and tossed into the boats.
 Viking travel was not all done with murderous intent; they are well known for colonizing westward as they farmed Iceland and possibly North America.
Viking travel was not all done with murderous intent; they are well known for colonizing westward as they farmed Iceland and possibly North America.

 Fenians invaded Canada no fewer than five times between 1866 and 1871. The idea was to bring pressure on Britain to withdraw from Ireland, so these attacks were directed toward British army forts, customs posts and other targets in Canada.
Fenians invaded Canada no fewer than five times between 1866 and 1871. The idea was to bring pressure on Britain to withdraw from Ireland, so these attacks were directed toward British army forts, customs posts and other targets in Canada.





 It was impossible to assemble the pieces of such a massive undertaking in secret, so an elaborate ruse called “Operation Fortitude” was launched to divert attention from the real objective. Fake field armies were assembled in Edinburgh, Scotland and the south coast of England, threatening attack on the coasts of Norway and the Pas de Calais. The real General George S. Patton was put in charge of the fake First US Army Group (FUSAG). The allied “Twenty Committee”, represented by its roman numerals “XX”, controlled a network of double agents, making the deception so complete that Hitler personally withheld critical reinforcements until long after they would have made a difference. It’s where we get the term “Double Cross”.
It was impossible to assemble the pieces of such a massive undertaking in secret, so an elaborate ruse called “Operation Fortitude” was launched to divert attention from the real objective. Fake field armies were assembled in Edinburgh, Scotland and the south coast of England, threatening attack on the coasts of Norway and the Pas de Calais. The real General George S. Patton was put in charge of the fake First US Army Group (FUSAG). The allied “Twenty Committee”, represented by its roman numerals “XX”, controlled a network of double agents, making the deception so complete that Hitler personally withheld critical reinforcements until long after they would have made a difference. It’s where we get the term “Double Cross”.





 Most of the political and military establishment lined up against Dreyfus, but the public outcry became furious after writer Émile Zola published his vehement open letter “J’accuse” (I accuse) in the Paris press in January 1898.
Most of the political and military establishment lined up against Dreyfus, but the public outcry became furious after writer Émile Zola published his vehement open letter “J’accuse” (I accuse) in the Paris press in January 1898.






 So it was that a vacation cruise to freedom became the “Voyage of the Damned”. MS St. Louis returned to Europe. Captain Schröder negotiated and schemed to find safe haven for his 907 passengers. Anything but return them to Nazi Germany. At one point, Schröder contemplated intentionally running aground off the coast of England. In the end, they all found refuge in Europe. 288 passengers were admitted by Great Britain, and 224 by France. 214 were accepted into Belgium and another 181 by the Netherlands.
So it was that a vacation cruise to freedom became the “Voyage of the Damned”. MS St. Louis returned to Europe. Captain Schröder negotiated and schemed to find safe haven for his 907 passengers. Anything but return them to Nazi Germany. At one point, Schröder contemplated intentionally running aground off the coast of England. In the end, they all found refuge in Europe. 288 passengers were admitted by Great Britain, and 224 by France. 214 were accepted into Belgium and another 181 by the Netherlands.
 As the story goes, it was 1853, at an upscale resort in Saratoga Springs New York. A wealthy and somewhat unpleasant customer sent his fried potatoes back to the kitchen, complaining that they were too soggy, and they didn’t have enough salt. George Crum, back in the kitchen, doesn’t seem to have been a very nice guy, himself. Crum thought he’d fix this guy, so he sliced some potatoes wafer-thin, fried them up and doused the hell out of them, with salt. Sending them out to the table and fully expecting the customer to choke on them, Crum was astonished to learn that the guy loved them. He ordered more, and George Crum decided to add “Saratoga Chips” to the menu. The potato chip was born.
As the story goes, it was 1853, at an upscale resort in Saratoga Springs New York. A wealthy and somewhat unpleasant customer sent his fried potatoes back to the kitchen, complaining that they were too soggy, and they didn’t have enough salt. George Crum, back in the kitchen, doesn’t seem to have been a very nice guy, himself. Crum thought he’d fix this guy, so he sliced some potatoes wafer-thin, fried them up and doused the hell out of them, with salt. Sending them out to the table and fully expecting the customer to choke on them, Crum was astonished to learn that the guy loved them. He ordered more, and George Crum decided to add “Saratoga Chips” to the menu. The potato chip was born.
 Lay began buying up small regional competitors at the same time that another company specializing in corn chips was doing the same. “Frito”, the Spanish word for “fried”, merged with Lay in 1961 to become – you got it – Frito-Lay. By 1965, the year Frito-Lay merged with Pepsi-Cola to become PepsiCo, Lay’s was the #1 potato chip brand in every state in America.
Lay began buying up small regional competitors at the same time that another company specializing in corn chips was doing the same. “Frito”, the Spanish word for “fried”, merged with Lay in 1961 to become – you got it – Frito-Lay. By 1965, the year Frito-Lay merged with Pepsi-Cola to become PepsiCo, Lay’s was the #1 potato chip brand in every state in America.

 Native American stickball had many variations, but the object was to hit a stake or other object with a “ball”. The ball was a stone wrapped in leather, handled with one or sometimes two sticks. There could be up to several hundred contestants to a team, and the defenders could employ any means they could think of to get at the ball, including hacking, slashing or any form of physical assault they liked. Lacerations and broken bones were commonplace, and it wasn’t unheard of that stickball players died on the field. The defending team could likewise employ any method they liked to keep the opposing team off of the ball carrier, and they played the game on a field that could range from 500 yards to several miles.
Native American stickball had many variations, but the object was to hit a stake or other object with a “ball”. The ball was a stone wrapped in leather, handled with one or sometimes two sticks. There could be up to several hundred contestants to a team, and the defenders could employ any means they could think of to get at the ball, including hacking, slashing or any form of physical assault they liked. Lacerations and broken bones were commonplace, and it wasn’t unheard of that stickball players died on the field. The defending team could likewise employ any method they liked to keep the opposing team off of the ball carrier, and they played the game on a field that could range from 500 yards to several miles.

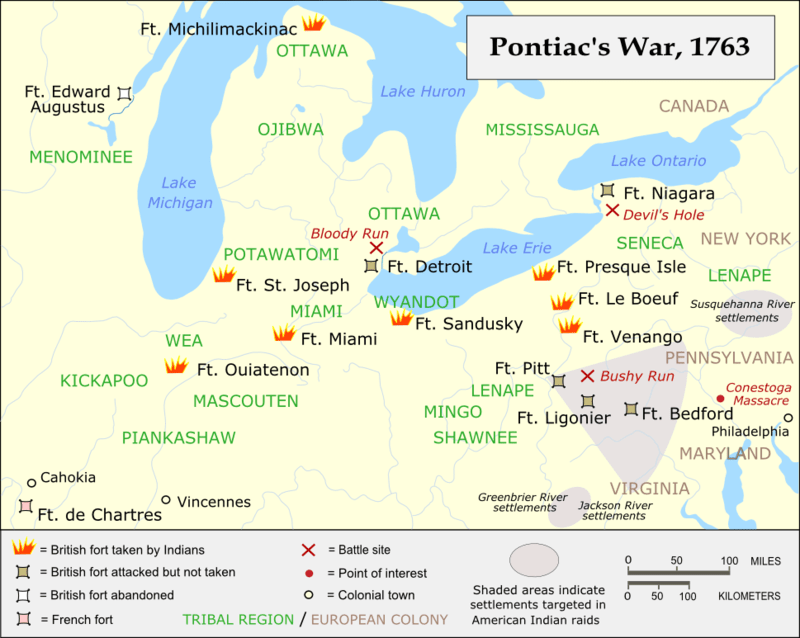
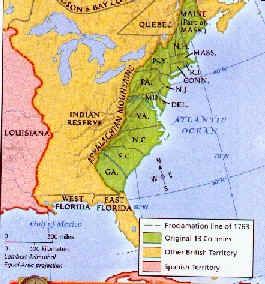 The British Royal Proclamation of October 7, 1763, drew a line between the British colonies and Indian lands, creating a vast Indian Reserve stretching from the Appalachians to the Mississippi River and from Florida to Newfoundland. For the Indian Nations, this was the first time that a multi-tribal effort had been launched against British expansion, the first time such an effort had not ended in defeat.
The British Royal Proclamation of October 7, 1763, drew a line between the British colonies and Indian lands, creating a vast Indian Reserve stretching from the Appalachians to the Mississippi River and from Florida to Newfoundland. For the Indian Nations, this was the first time that a multi-tribal effort had been launched against British expansion, the first time such an effort had not ended in defeat.



 The results of the Feuerwalze were devastating, if not predictable. Allied lines were smashed as German armies poured through, taking 19 kilometers in three days and reaching the Marne River, 50 miles from Paris. On May 31, a dogged defense by the US 3rd Infantry Division turned the German advance at Château-Thierry, and toward Belleau Wood.
The results of the Feuerwalze were devastating, if not predictable. Allied lines were smashed as German armies poured through, taking 19 kilometers in three days and reaching the Marne River, 50 miles from Paris. On May 31, a dogged defense by the US 3rd Infantry Division turned the German advance at Château-Thierry, and toward Belleau Wood.

You must be logged in to post a comment.