With increasing tensions between the Unites States and the empire of Japan, the “China Marines” of the Fourth Marine Regiment, “The Oldest and the Proudest”, departed Shanghai for the Philippines on November 27-28, 1941. The first elements arrived at Subic Bay on November 30.
A week later and 5,000 miles to the east, the radio crackled to life in the early – morning hours of December 7. “Air raid on Pearl Harbor. This is no drill!”
Military forces of Imperial Japan appeared unstoppable in the early months of WWII, attacking first Thailand, then the British possessions of Malaya, Singapore and Hong Kong, as well as US military bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam and the Philippines.
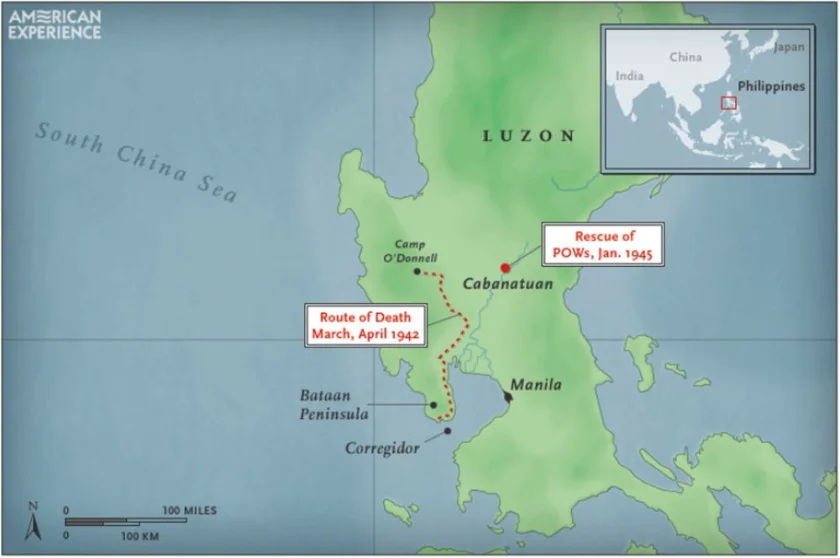
On January 7, Japanese forces attacked the Bataan peninsula. The Fourth Marines, under Army command, were ordered to help strengthen defenses on the “Gibraltar of the East”, the heavily fortified island of Corregidor.
The prize was nothing less than the finest natural harbor in the Asian Pacific, Manila Bay, the Bataan Peninsula forming the lee shore and Corregidor and nearby Caballo Islands standing at the mouth, dividing the entrance into two channels. Before the Japanese invasion was to succeed, Bataan and Corregidor must be destroyed.
 The United States was grossly unprepared to fight a World War in 1942. The latest iteration of “War Plan Orange” (WPO-3) called for delaying tactics in the event of war with Japan, buying time to gather US Naval assets to sail for the Philippines. The problem was, there was no fleet to gather. The flower of American pacific power in the pacific, lay at the bottom of Pearl Harbor. Allied war planners turned their attention to defeating Adolf Hitler.
The United States was grossly unprepared to fight a World War in 1942. The latest iteration of “War Plan Orange” (WPO-3) called for delaying tactics in the event of war with Japan, buying time to gather US Naval assets to sail for the Philippines. The problem was, there was no fleet to gather. The flower of American pacific power in the pacific, lay at the bottom of Pearl Harbor. Allied war planners turned their attention to defeating Adolf Hitler.
General Douglas MacArthur abandoned Corregidor on March 12, departing the “Alamo of the Pacific” with the words, “I shall return”. Some 90,000 American and Filipino troops were left behind without food, supplies or support with which to fight off the onslaught of the Japanese 14th Army, under the command of Lieutenant General Masaharu Homma.
Battered by wounds and starvation, decimated by all manner of tropical disease and parasite, the 75,000 “Battling Bastards of Bataan” fought on until they could fight no more. Some 75,000 American and Filipino fighters were surrendered with the Bataan peninsula on April 9, only to begin a 65-mile, five-day slog into captivity through the unbearable heat and humidity, of the Philippine jungle.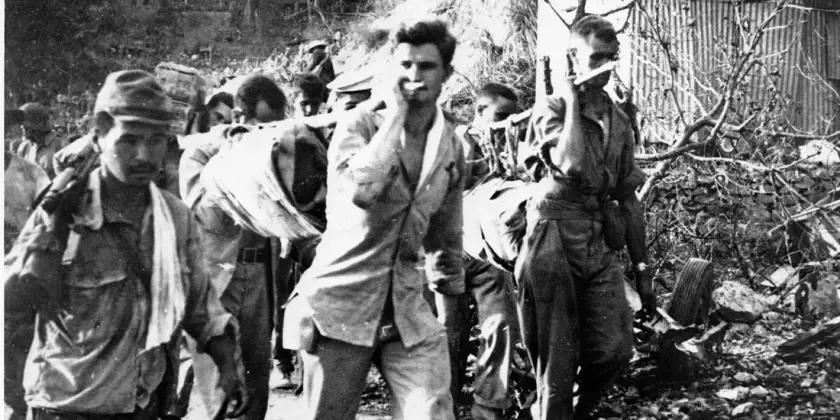 The Japanese were sadistic. Guards would beat marchers and bayonet those too weak to walk. Tormented by a thirst few among us can even imagine, men were made to stand for hours under a relentless sun, standing by a stream from which none were permitted to drink. The man who broke ranks and dove for the water was clubbed or bayoneted to death, on the spot. Japanese tanks would swerve out of their way to run over anyone who had fallen and was too slow in getting up. Some were burned alive, others buried alive. Already crippled from tropical disease and starving from the long siege of Luzon, wanton killing and savage abuse took the lives of some 500 – 650 Americans and between 5,000 – 18,000 Filipinos.
The Japanese were sadistic. Guards would beat marchers and bayonet those too weak to walk. Tormented by a thirst few among us can even imagine, men were made to stand for hours under a relentless sun, standing by a stream from which none were permitted to drink. The man who broke ranks and dove for the water was clubbed or bayoneted to death, on the spot. Japanese tanks would swerve out of their way to run over anyone who had fallen and was too slow in getting up. Some were burned alive, others buried alive. Already crippled from tropical disease and starving from the long siege of Luzon, wanton killing and savage abuse took the lives of some 500 – 650 Americans and between 5,000 – 18,000 Filipinos.
For those who survived the “Bataan Death March”, this was only the beginning of their ordeal.
 United States Marine Corps 1st Lieutenant Austin Shofner came ashore back in November, with the 4th Marines. Shofner and his fellow leathernecks engaged the Japanese as early as December 12 and received their first taste of aerial bombardment, on December 29. Promoted to Captain and placed in command of Headquarters Company, Shofner received two Silver Stars by April 15 in near-constant defense against aerial attack.
United States Marine Corps 1st Lieutenant Austin Shofner came ashore back in November, with the 4th Marines. Shofner and his fellow leathernecks engaged the Japanese as early as December 12 and received their first taste of aerial bombardment, on December 29. Promoted to Captain and placed in command of Headquarters Company, Shofner received two Silver Stars by April 15 in near-constant defense against aerial attack.
For three months, defenders on Corregidor were required to resist near constant aerial, naval and artillery bombardment. All that on two scant water rations and a meager food allotment of only 30 ounces per day.
I don’t know about you, but I’ve eaten Steaks bigger than 30 ounces.
Beset as they were, seven private maritime vessels attempted to run the Japanese gauntlet, loaded with food and supplies. The MV Princessa commanded by 3rd Lieutenant Zosimo Cruz (USAFFE), was the only ship to arrive in Corregidor.
Japanese artillery bombardment intensified, following the fall of Bataan. Cavalry horses killed in the onslaught were dragged into tunnels and caves, and consumed. Japanese aircraft dropped 1,701 bombs in the tiny island during 614 sorties, armed with some 365-tons of high explosive. On May 4 alone, an estimated 16,000 shells hit the little island.

The final assault beginning May 5 met with savage resistance, but the outcome was never in doubt. General Jonathan Wainwright was in overall command of the defenders on Corregidor. Some 11,000 men comprised of United States Marines, Army and Navy and an assemblage of Filipino fighters. The “Malinta Tunnel” alone contained over a thousand, so sick or wounded as to be helpless. Fewer than half had even received training in ground combat techniques.
All were starved, sick, utterly exhausted. The 4th Marines was shattered, no longer an effective fighting force. With the May 6 landing of Japanese tanks, General Wainwright elected the preservation of life over continued slaughter in the defense of a hopeless position. Maine Colonel Samuel Howard ordered the regimental and national colors burned to prevent their capture, as Wainwright sent a radio message to President Roosevelt:
“There is a limit of human endurance, and that point has long been passed.”
Isolated pockets of marines fought on for four hours until at last, all was still. Two officers were sent forward with a white flag, to carry the General’s message of surrender. It was 1:30pm, May 6, 1941. Nearly 150,000 Allied soldiers were taken captive by the Japanese Empire during World War 2. Clad in unspeakably filthy rags they were fed a mere 600 calories per day of fouled rice, supplemented only by the occasional insect or bird or rodent unlucky enough to fall into desperate hands. Diseases like malaria were all but universal as gross malnutrition led to loss of vision and unrelenting nerve pain. Dysentery, a hideously infectious disease of the large intestine reduced grown men to animated skeletons. Mere scratches resulted in grotesque tropical ulcers up to a foot in length exposing living bone and rotting flesh to swarms of ravenous insects.
Nearly 150,000 Allied soldiers were taken captive by the Japanese Empire during World War 2. Clad in unspeakably filthy rags they were fed a mere 600 calories per day of fouled rice, supplemented only by the occasional insect or bird or rodent unlucky enough to fall into desperate hands. Diseases like malaria were all but universal as gross malnutrition led to loss of vision and unrelenting nerve pain. Dysentery, a hideously infectious disease of the large intestine reduced grown men to animated skeletons. Mere scratches resulted in grotesque tropical ulcers up to a foot in length exposing living bone and rotting flesh to swarms of ravenous insects.
The death rate for western prisoners was 27.1% across 130 Japanese prison encampments. Seven times the death toll for allied prisoners in Nazi Germany, or Fascist Italy. Given such cruel conditions it’s a wonder anyone escaped at all but it did happen. One time.
Given such cruel conditions it’s a wonder anyone escaped at all but it did happen. One time.
Austin Schofner and his group were moved from camp to camp. Bilibid. Cabanatuan. Davao. Throughout early 1943, Schofner and others would steal away from work details to squirrel away small caches of food and tools, in the jungle. Nine fellow Marines and two Filipino soldiers were in on the scheme. On April 4, the 12 men quietly slipped away from work parties.
Over the long hours of April 5-6, the group crept through the jungle, dodging enemy patrols and managing to avoid detection, arriving on the 7th at a remote Filipino Guerrilla outpost. Guided by wild mountain tribesmen of the Ata Manobo, the Marines rejoined the 110th Division, 10th Military District, at this time conducting guerrilla operations against the Japanese occupiers.
Emaciated, sick and weak, these men had reached the end of an ordeal a year and a half in the making. It would be understandable if they were to seek out the relative safety of a submarine bound to Australia, but no. Those physically able to do so joined the guerrillas in fighting the Japanese.
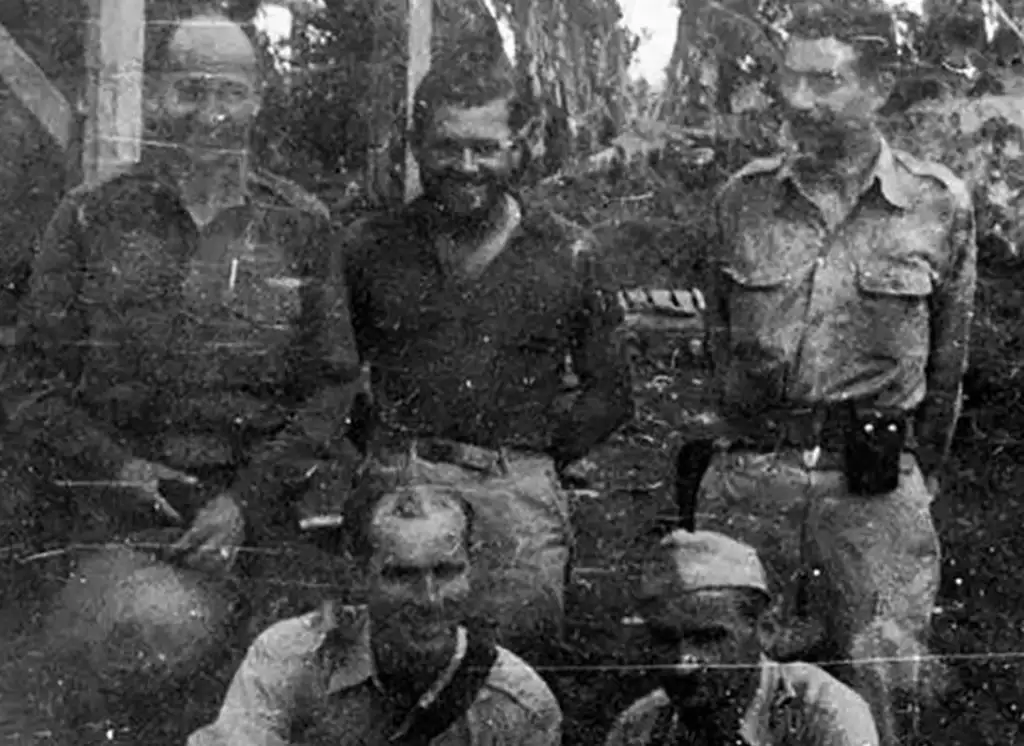

Austin Shofner and his Marines were evacuated that November, aboard the submarine USS Narwhal. For the first time, Japanese atrocities came to light. The Death March, the torture, mistreatment and summary execution of Allied POWs. The public was outraged, leading to a change in Allied war strategy. No longer would the war in the Pacific take a back seat to the effort to destroy the Nazi war machine.

Now-Colonel Shofner volunteered to return to the Pacific where his experience helped with the rescue of 500 prisoners of the infamous POW camp at Cabanatuan on January 30, 1945.
An American military tribunal conducted after the war held Lieutenant General Homma Masaharu, commander of the Japanese invasion forces in the Philippines, guilty of war crimes. He was executed by firing squad on April 3, 1946.
The Davao Dozen conducted the only successful escape from a Japanese Prison camp in all World War 2. They deserve that we remember their names.
The only successful escape from a Japanese Prisoner of war camp in all World War 2, The “Davao Dozen” include Here are the names of the Americans in the Davao Dozen:
Second Lieutenant Leo Boelens
First Lieutenant Michiel Dobervich
Captain William Edwin Dyess
Second Lieutenant Samuel Grashio
First Lieutenant Jack Hawkins
Lieutenant Commander Melvyn McCoy
Sergeant Paul Marshall
Major Stephen Mellnik
Captain Austin Shofner
Sergeant Robert Spielman
Benigno de la Crus
Victorio Jumarong
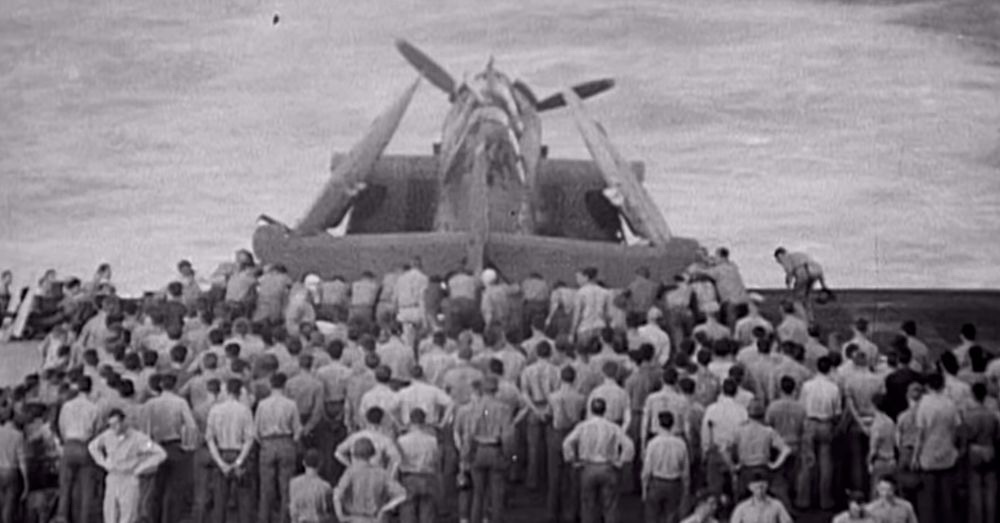












 Germany needed air supremacy before “Operation Sea Lion”, the amphibious invasion of England, could begin. Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring said he would have it in four days.
Germany needed air supremacy before “Operation Sea Lion”, the amphibious invasion of England, could begin. Luftwaffe commander Hermann Göring said he would have it in four days.


 Czechoslovakia fell to the Nazis on the Ides of March, 1939, Czech armed forces having been ordered to offer no resistance. Some 4,000 Czech soldiers and airmen managed to get out, most escaping to neighboring Poland.
Czechoslovakia fell to the Nazis on the Ides of March, 1939, Czech armed forces having been ordered to offer no resistance. Some 4,000 Czech soldiers and airmen managed to get out, most escaping to neighboring Poland.
 British military authorities were slow to recognize the flying skills of the Polskie Siły Powietrzne (Polish Air Forces), the first fighter squadrons only seeing action in the third phase of the Battle of Britain. Despite the late start, Polish flying skills proved superior to those of less-experienced Commonwealth pilots. The 303rd Polish fighter squadron became the most successful RAF fighter unit of the period, its most prolific flying ace being Czech Sergeant Josef František. He was killed in action in the last phase of the Battle of Britain, the day after his 26th birthday.
British military authorities were slow to recognize the flying skills of the Polskie Siły Powietrzne (Polish Air Forces), the first fighter squadrons only seeing action in the third phase of the Battle of Britain. Despite the late start, Polish flying skills proved superior to those of less-experienced Commonwealth pilots. The 303rd Polish fighter squadron became the most successful RAF fighter unit of the period, its most prolific flying ace being Czech Sergeant Josef František. He was killed in action in the last phase of the Battle of Britain, the day after his 26th birthday.






 So it was that a vacation cruise to freedom became the “Voyage of the Damned”. MS St. Louis returned to Europe. Captain Schröder negotiated and schemed to find safe haven for his 907 passengers. Anything but return them to Nazi Germany. At one point, Schröder contemplated intentionally running aground off the coast of England. In the end, they all found refuge in Europe. 288 passengers were admitted by Great Britain, and 224 by France. 214 were accepted into Belgium and another 181 by the Netherlands.
So it was that a vacation cruise to freedom became the “Voyage of the Damned”. MS St. Louis returned to Europe. Captain Schröder negotiated and schemed to find safe haven for his 907 passengers. Anything but return them to Nazi Germany. At one point, Schröder contemplated intentionally running aground off the coast of England. In the end, they all found refuge in Europe. 288 passengers were admitted by Great Britain, and 224 by France. 214 were accepted into Belgium and another 181 by the Netherlands.
 In May of 1940 the British Expeditionary Force and what remained of French forces occupied a sliver of land along the English Channel. Field Marshall Gerd von Rundstedt called a halt of the German armored advance on May 24, while Hermann Göring urged Hitler to stop the ground assault, let the Luftwaffe finish the destruction of Allied forces. On the other side of the channel, Admiralty officials combed every boatyard they could find for boats to ferry their people off of the beach.
In May of 1940 the British Expeditionary Force and what remained of French forces occupied a sliver of land along the English Channel. Field Marshall Gerd von Rundstedt called a halt of the German armored advance on May 24, while Hermann Göring urged Hitler to stop the ground assault, let the Luftwaffe finish the destruction of Allied forces. On the other side of the channel, Admiralty officials combed every boatyard they could find for boats to ferry their people off of the beach.





 Hess was an early and ardent proponent of Nazi ideology. A True Believer. He was at Hitler’s side during the failed revolution of 1923, the “Beer Hall Putsch”. He served time with Hitler in prison, and helped him write his political opus “Mein Kampf” (My Struggle). Hess was appointed to Hitler’s cabinet when the National Socialist German Workers’ Party seized power in 1933, becoming Deputy Führer, #3 after Hermann Göring and Hitler himself. Hess signed many statutes into law, including the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, depriving the Jews of Germany of their rights and property.
Hess was an early and ardent proponent of Nazi ideology. A True Believer. He was at Hitler’s side during the failed revolution of 1923, the “Beer Hall Putsch”. He served time with Hitler in prison, and helped him write his political opus “Mein Kampf” (My Struggle). Hess was appointed to Hitler’s cabinet when the National Socialist German Workers’ Party seized power in 1933, becoming Deputy Führer, #3 after Hermann Göring and Hitler himself. Hess signed many statutes into law, including the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, depriving the Jews of Germany of their rights and property.



 In the latter half of WWII, Imperial Japanese military thinkers conceived the fūsen bakudan or “fire balloon”, a hydrogen filled balloon device designed to ride the jet stream, using sand ballast and a valve system to navigate the weapon system onto the North American continent.
In the latter half of WWII, Imperial Japanese military thinkers conceived the fūsen bakudan or “fire balloon”, a hydrogen filled balloon device designed to ride the jet stream, using sand ballast and a valve system to navigate the weapon system onto the North American continent.




 Itter Castle appeared in the land records of the Austrian Tyrol as early as 1240. When Germany annexed Austria in 1938, Schloss Itter was first leased and later requisitioned outright by the German government, for unspecified “Official use”.
Itter Castle appeared in the land records of the Austrian Tyrol as early as 1240. When Germany annexed Austria in 1938, Schloss Itter was first leased and later requisitioned outright by the German government, for unspecified “Official use”.

 It was late afternoon as the convoy left for Castle Itter. Leaving Boche Buster and a few Infantry to guard the largest bridge into town. What remained of the convoy fought its way through its last SS roadblock in the early evening, roaring across the last bridge and lurching to a stop in front of Itter’s gate as night began to fall. Itter’s prisoners looked on in dismay. They had expected a column of American tanks and a heavily armed infantry force. What they had here, was a single tank with seven Americans, and a truckload of armed Germans.
It was late afternoon as the convoy left for Castle Itter. Leaving Boche Buster and a few Infantry to guard the largest bridge into town. What remained of the convoy fought its way through its last SS roadblock in the early evening, roaring across the last bridge and lurching to a stop in front of Itter’s gate as night began to fall. Itter’s prisoners looked on in dismay. They had expected a column of American tanks and a heavily armed infantry force. What they had here, was a single tank with seven Americans, and a truckload of armed Germans. concentration camp administration for the Third Reich and some of the most fanatical soldiers of WWII. Even at this late date SS units were putting up fierce resistance across northern Austria. 100-150 of them attacked on the morning of May 5. Fighting was furious around Castle Itter, the one Sherman providing machine-gun fire support until it was destroyed by a German 88mm gun. By early afternoon Lee was able to get a desperate plea for reinforcements through to the 142nd Infantry, before being cut off. Aware that he’d been unable to give complete information on the enemy’s troop strength and disposition, Lee accepted Jean Borotra’s gallant offer of assistance.
concentration camp administration for the Third Reich and some of the most fanatical soldiers of WWII. Even at this late date SS units were putting up fierce resistance across northern Austria. 100-150 of them attacked on the morning of May 5. Fighting was furious around Castle Itter, the one Sherman providing machine-gun fire support until it was destroyed by a German 88mm gun. By early afternoon Lee was able to get a desperate plea for reinforcements through to the 142nd Infantry, before being cut off. Aware that he’d been unable to give complete information on the enemy’s troop strength and disposition, Lee accepted Jean Borotra’s gallant offer of assistance. Literally vaulting over the castle wall, the tennis star ran through a gauntlet of SS strongpoints and ambushes to deliver his message, before donning an American uniform to help fight through to the castle’s defenders. The relief force arrived at around 4pm, as defenders were firing their last ammunition.
Literally vaulting over the castle wall, the tennis star ran through a gauntlet of SS strongpoints and ambushes to deliver his message, before donning an American uniform to help fight through to the castle’s defenders. The relief force arrived at around 4pm, as defenders were firing their last ammunition.
 Isoroku Takano was born in Niigata, the son of a middle-ranked samurai of the Nagaoka Domain. His first name “Isoroku”, translating as “56”, refers to his father’s age at the birth of his son. At this time, it was common practice that samurai families without sons would “adopt” suitable young men, in order to carry on the family name, rank, and the income that came with it. The young man so adopted would carry the family name. So it was that Isoroku Takano became Isoroku Yamamoto in 1916, at the age of 32.
Isoroku Takano was born in Niigata, the son of a middle-ranked samurai of the Nagaoka Domain. His first name “Isoroku”, translating as “56”, refers to his father’s age at the birth of his son. At this time, it was common practice that samurai families without sons would “adopt” suitable young men, in order to carry on the family name, rank, and the income that came with it. The young man so adopted would carry the family name. So it was that Isoroku Takano became Isoroku Yamamoto in 1916, at the age of 32.
 Many believed that Yamamoto’s career was finished when his old adversary Hideki Tōjō ascended to the Prime Ministership in 1941. Yet there was none better to run the combined fleet. When the pro-war faction took control of the Japanese government, he bowed to the will of his superiors. It was Isoroku Yamamoto who was tasked with planning the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Many believed that Yamamoto’s career was finished when his old adversary Hideki Tōjō ascended to the Prime Ministership in 1941. Yet there was none better to run the combined fleet. When the pro-war faction took control of the Japanese government, he bowed to the will of his superiors. It was Isoroku Yamamoto who was tasked with planning the attack on Pearl Harbor. American carrier based Torpedo bombers were slaughtered in their attack, with 36 out of 42 shot down. Yet Japanese defenses had been caught off-guard, their carriers busy rearming and refueling planes when American dive-bombers arrived.
American carrier based Torpedo bombers were slaughtered in their attack, with 36 out of 42 shot down. Yet Japanese defenses had been caught off-guard, their carriers busy rearming and refueling planes when American dive-bombers arrived. Midway was a disaster for the Imperial Japanese navy. The carriers Akagi, Kaga, Soryu and Hiryu, the entire strength of the task force, went to the bottom. The Japanese also lost the heavy cruiser Mikuma, along with 344 aircraft and 5,000 sailors. Much has been made of the loss of Japanese aircrews at Midway, but two-thirds of them survived. The greater long term disaster, may have been the loss of all those trained aircraft mechanics and ground crew who went down with their carriers.
Midway was a disaster for the Imperial Japanese navy. The carriers Akagi, Kaga, Soryu and Hiryu, the entire strength of the task force, went to the bottom. The Japanese also lost the heavy cruiser Mikuma, along with 344 aircraft and 5,000 sailors. Much has been made of the loss of Japanese aircrews at Midway, but two-thirds of them survived. The greater long term disaster, may have been the loss of all those trained aircraft mechanics and ground crew who went down with their carriers. tour throughout the South Pacific. US naval intelligence intercepted and decoded his schedule. The order for “Operation Vengeance” went down the chain of command from President Roosevelt to Secretary of the Navy Frank Knox to Naval Operations Admiral Ernest King to Admiral Chester Nimitz at Pearl Harbor. Sixteen Lockheed P-38 Lightnings, the only fighters capable of the ranges involved, were dispatched from Guadalcanal on April 17 with the order: “Get Yamamoto”.
tour throughout the South Pacific. US naval intelligence intercepted and decoded his schedule. The order for “Operation Vengeance” went down the chain of command from President Roosevelt to Secretary of the Navy Frank Knox to Naval Operations Admiral Ernest King to Admiral Chester Nimitz at Pearl Harbor. Sixteen Lockheed P-38 Lightnings, the only fighters capable of the ranges involved, were dispatched from Guadalcanal on April 17 with the order: “Get Yamamoto”. intercepted over Rabaul on April 18, 1943. Knowing only that his target was “an important high value officer”, 1st Lieutenant Rex Barber opened up on the first Japanese transport until smoke billowed from its left engine. Yamamoto’s body was found in the wreckage the following day with a .50 caliber bullet wound in his shoulder, another in his head. He was dead before he hit the ground.
intercepted over Rabaul on April 18, 1943. Knowing only that his target was “an important high value officer”, 1st Lieutenant Rex Barber opened up on the first Japanese transport until smoke billowed from its left engine. Yamamoto’s body was found in the wreckage the following day with a .50 caliber bullet wound in his shoulder, another in his head. He was dead before he hit the ground.

 Melvin attended a year at Brooklyn College before being drafted into the Army, in WWII. After attending Army Specialized Training at VMI, Corporal Kaminsky joined the 1104th Combat Engineers Battalion, 78th Infantry Division in the European theater. There, he served through the end of the war. Most of his work was in finding and defusing explosives, though on five occasions his unit had to drop their tools and fight as Infantry.
Melvin attended a year at Brooklyn College before being drafted into the Army, in WWII. After attending Army Specialized Training at VMI, Corporal Kaminsky joined the 1104th Combat Engineers Battalion, 78th Infantry Division in the European theater. There, he served through the end of the war. Most of his work was in finding and defusing explosives, though on five occasions his unit had to drop their tools and fight as Infantry. German soldiers singing a beer hall song, from the other side. Kaminsky grabbed a bullhorn and serenaded the Germans back, singing them an old tune that Al Jolson used to perform in black face, “Toot Toot Tootsie, Goodbye”. Polite applause could be heard from across the river, afterward. I can’t imagine many Allied soldiers ever tried to serenade their Nazi adversaries during World War II. The ones who actually pulled it off must number, precisely, one.
German soldiers singing a beer hall song, from the other side. Kaminsky grabbed a bullhorn and serenaded the Germans back, singing them an old tune that Al Jolson used to perform in black face, “Toot Toot Tootsie, Goodbye”. Polite applause could be heard from across the river, afterward. I can’t imagine many Allied soldiers ever tried to serenade their Nazi adversaries during World War II. The ones who actually pulled it off must number, precisely, one.

 Marvin Hamlisch, Jonathan Tunick, Mike Nichols, Whoopi Goldberg, Scott Rudin, and Robert Lopez. As of this date, Brooks only needs another Oscar to be the first “Double EGOT” in history.
Marvin Hamlisch, Jonathan Tunick, Mike Nichols, Whoopi Goldberg, Scott Rudin, and Robert Lopez. As of this date, Brooks only needs another Oscar to be the first “Double EGOT” in history.
You must be logged in to post a comment.