On June 6, 2019, CNN reported on the alarming number of US Military service deaths in training accidents, and other “circumstances unrelated to war. “Since 2006” they wrote, “a total of 16,652 active-duty personnel and mobilized reservists have died while serving in the US armed forces. Seventy-three percent of these casualties occurred under circumstances unrelated to war”.
We would hope that those to whom we entrust the lives of our best and brightest would learn and adjust in response, that those lives not be lost in vain. War is, after all, a dangerous business.
Be that as it may no service member’s life lost in ‘circumstances unrelated to war’ is any less valuable, any less heroic, than those who died facing the adversary.
Permit me to speak then, of “Exercise Tiger.” A dress rehearsal for the largest seaborne invasion in history, gone terribly wrong. Their sacrifice taught important lessons and saved the lives of unknown legions of heroes. They, too, have earned the right to be remembered.
The largest amphibious attack in history began on June 6, 1944, on the northern coast of France. British and Canadian forces came ashore at beaches codenamed Gold, Juno and Sword. Americans faced light opposition at Utah Beach while heavy resistance at Omaha Beach resulted in over 2,000 American casualties.

By the end of day, some 156,000 Allied troops had stormed the beaches of Normandy. Within a week that number would rise to 326,000 troops, more than 50,000 vehicles and over 100,000 tons of equipment.
Overlord’s success resulted from lessons learned from the largest amphibious training exercise of the war, the six phases of “Operation Fabius”, itself following the unmitigated disaster of a training exercise that killed more Americans than the actual landing at Utah beach.
Slapton is a village and civil parish in the River Meadows of Devon County, where the southwest coast of England meets the English Channel. Archaeological evidence suggests human habitation from at least the bronze age. The “Domesday Book”, the recorded manuscript of the “Great Survey” of England and Wales completed in 1086 by order of William the Conqueror, names the place as “Sladone”, with a population of 200.
In late 1943, 750 families, some 3,000 locals, were evacuated with their livestock to make way for “Operation Tiger”, a D-Day landing rehearsal scheduled for the following spring. Some had never so much as left their home village.
Thousands of US military personnel were moved into the region during the winter of 1943-44. The area was mined and bounded with barbed wire and patrolled by sentries. Secrecy was so tight that even those in surrounding villages had no idea of what was happening.
Exercise Tiger was scheduled to begin on April 22, covering all aspects of the “Force U” landing on Utah beach and culminating in a live-fire beach landing at Slapton Sands at first light, on April 27.
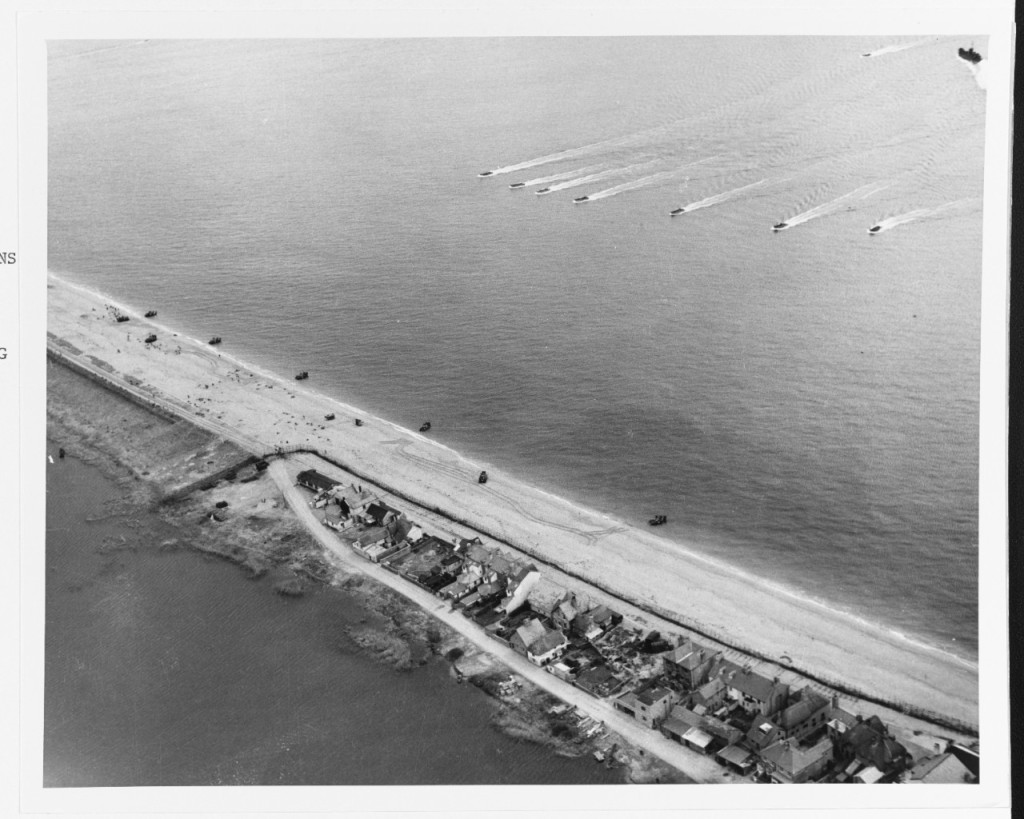

Nine large tank landing ships (LSTs) shoved off with 30,000 troops on the evening of the 26th, simulating the overnight channel crossing. Live ammunition was used in the exercise, to harden troops off to the sights, sounds and smells of actual battle. Naval bombardment was to commence 50 minutes before H-Hour, however delays resulted in landing forces coming under direct naval bombardment. An unknown number were killed in this “friendly fire” incident. Fleet rumors put the number as high as 450.
Two Royal Navy Corvettes, HMS Azalea and Scimitar, were to guard the exercise from German “Schnellboots” (“S-Boots”), the fast attack craft based out of Cherbourg.
Scimitar withdrew for repairs following a collision with an LST on the 27th. In the early morning darkness of the following day, the single corvette was leading 8 LSTs carrying vehicles and combat engineers of the 1st Engineer Special Brigade through Lyme Bay, when the convoy was spotted by a nine vessel S-Boat patrol.
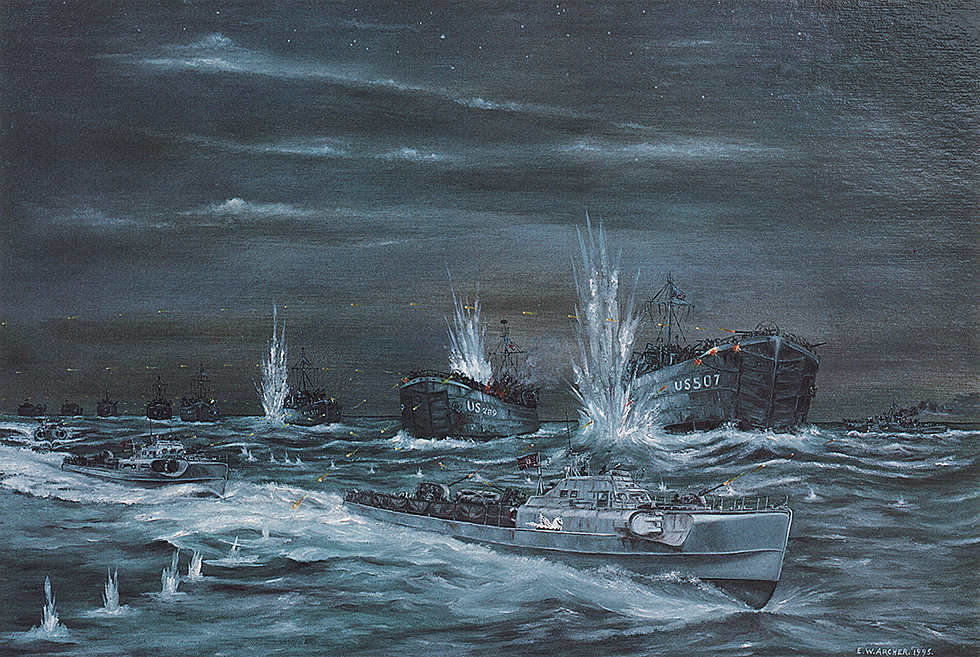

8 landing craft in single-file didn’t have a chance against fast-attack craft capable of 55mph. LST-531 was torpedoed and sunk in minutes, killing 424 Army and Navy personnel. LST-507 suffered the same fate, with the loss of 202. LST-289 made it to shore in flames, with the loss of 123. LST-511 was damaged in yet another friendly fire incident. Unable to wear their lifebelts correctly due to the large backpacks they wore, many men placed them around their waists. That only turned them upside down. That is how they died, thrashing in the water with their legs above the waves. Dale Rodman, who survived the sinking of LST-507, said, “The worst memory I have is setting off in the lifeboat away from the sinking ship and watching bodies float by.”
Survivors were sworn to secrecy due to official embarrassment, and the possibility of revealing the real invasion, scheduled for June. Ten officers with high level clearance were killed in the incident, but no one knew that for sure until their bodies were recovered. The D-Day invasion was nearly called off, because any of them could have been captured alive, revealing secrets during German interrogation and torture.
There’s a surprising amount of confusion about the final death toll. Estimates range from 639 to 946, nearly five times the number killed in the actual Utah Beach landing. Some or all the personnel from that damaged LST may have been aboard the other 8 on the 28th, and log books went down along with everything else. Many of the remains have never been found.
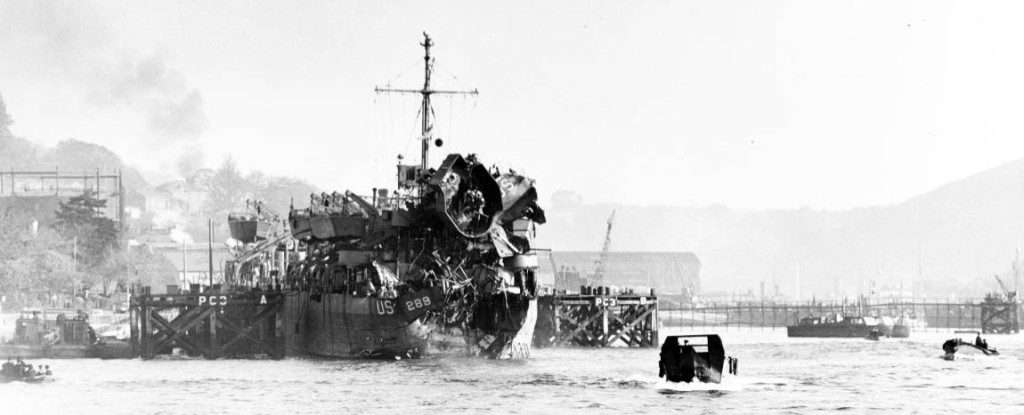

That number would surely have been higher, had not Captain John Doyle disobeyed orders and turned his LST-515 around, plucking 134 men from the frigid water.
Today, the Exercise Tiger disaster is all but forgotten. Some have charged official cover-ups, though information from SHAEF press releases appeared in the August edition of Stars & Stripes. At least three books contain the information. It seems more likely that the immediate need for secrecy and subsequent D-Day invasion swallowed the Tiger disaster, whole. History has a way of doing that.

Some of Slapton’s residents came home to rebuild their lives after the war, but many never returned. In the early 1970s, Devon resident and civilian Ken Small discovered an artifact of the Tiger exercise, while beachcombing on Slapton Sands. With little or no help from either the American or British governments, Small purchased rights from the U.S. Government to a submerged Sherman tank from the 70th Tank Battalion. The tank was raised in 1984 with the help of local residents and dive shops, and now stands as a memorial to Exercise Tiger. Not far away is a memorial to the villagers who never came home.
A plaque was erected at Arlington National Cemetery in 1995, inscribed with the words “Exercise Tiger Memorial”. A 5,000-pound stern anchor bears silent witness to Exercise Tiger in Mexico, Missouri, as does an M4 Sherman tank at Fort Rodman Park in New Bedford, Massachusetts.

In 1676, Isaac Newton wrote to rival Robert Hooke: “…If I have seen a little further, it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.”
Today, we celebrate ‘The Boys of Pointe du Hoc’ and all the heroes of D-Day, for it is they who broke down the door to Fortress Europe. It is well that we should do this, and to remember. They, too, have stood on the shoulders of giants.
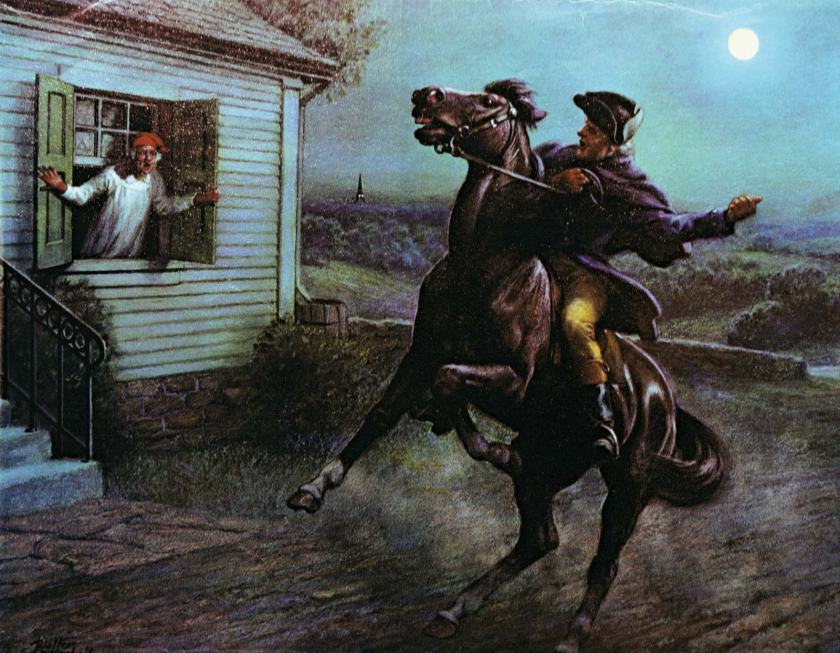






























 Revere himself covered barely 12 miles before being captured, his horse confiscated to replace the tired mount of a British sergeant. Revere would finish his “ride” on foot, arriving at sunrise on the 19th to witness the last moments of the battle on Lexington Green.
Revere himself covered barely 12 miles before being captured, his horse confiscated to replace the tired mount of a British sergeant. Revere would finish his “ride” on foot, arriving at sunrise on the 19th to witness the last moments of the battle on Lexington Green.



 General David Wooster was mortally wounded at the Battle of Ridgefield, moments after shouting “Come on my boys! Never mind such random shots!” Today, an archway marks the entrance to Wooster Square, in the East Rock Neighborhood of New Haven.
General David Wooster was mortally wounded at the Battle of Ridgefield, moments after shouting “Come on my boys! Never mind such random shots!” Today, an archway marks the entrance to Wooster Square, in the East Rock Neighborhood of New Haven.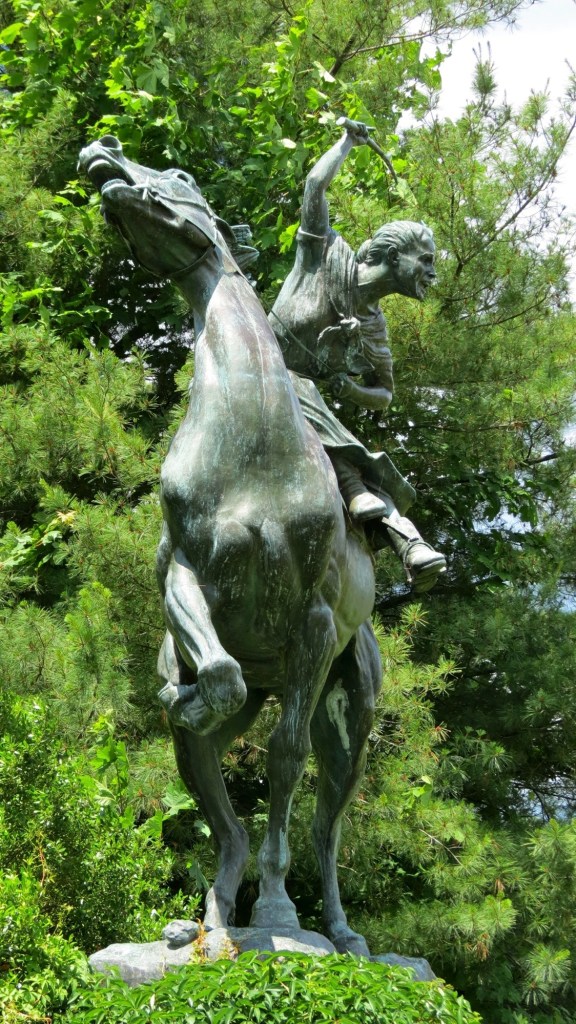 

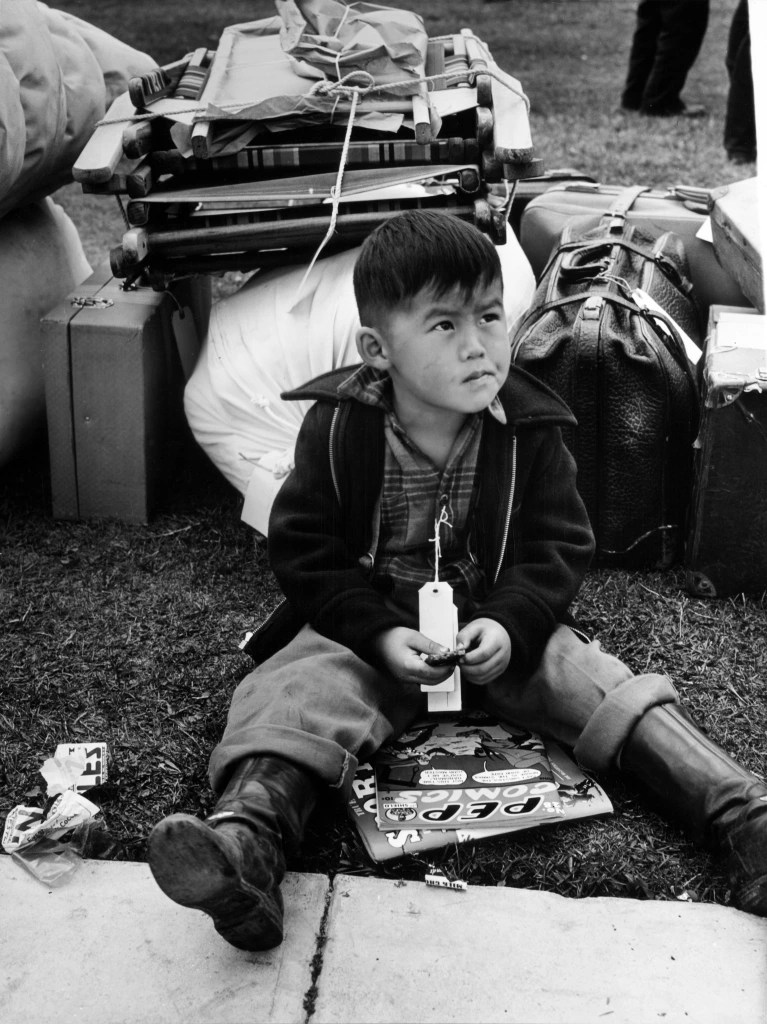
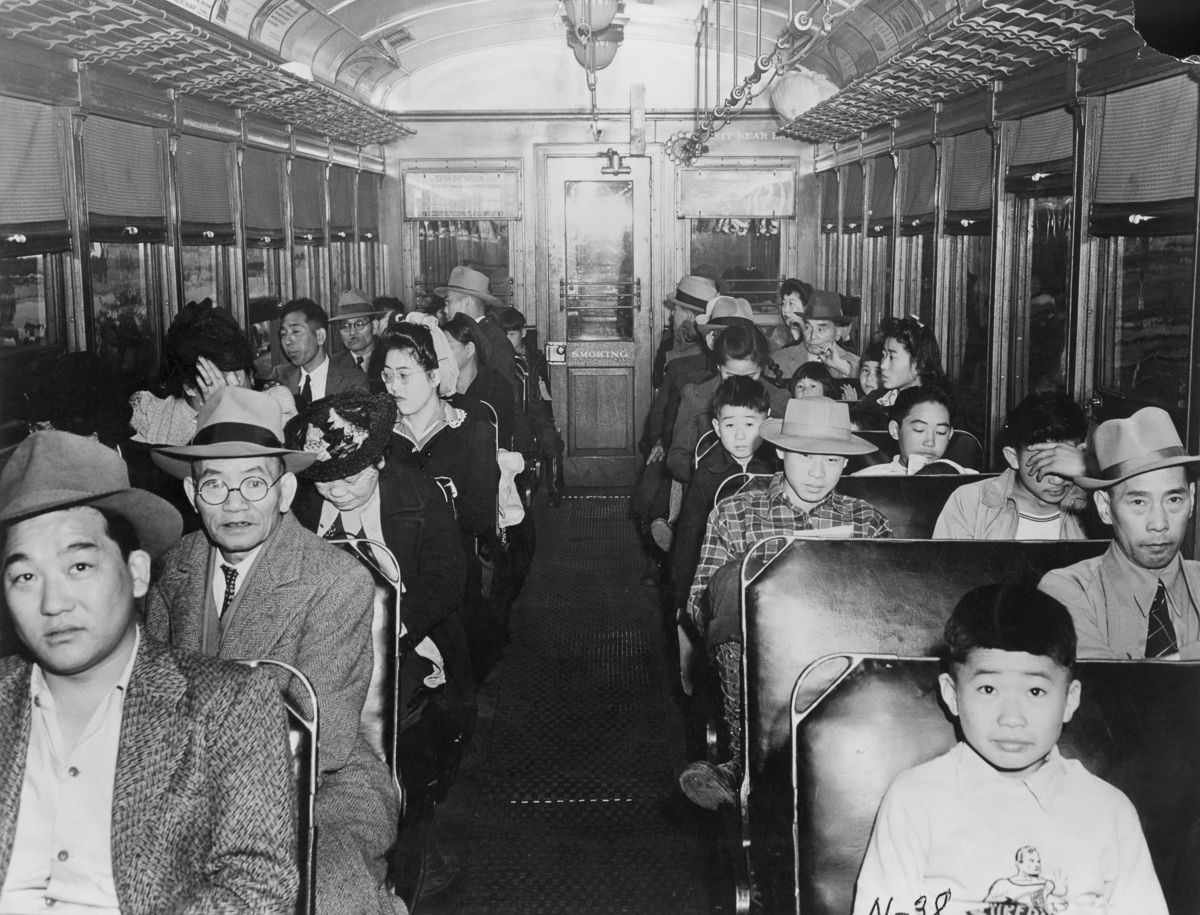
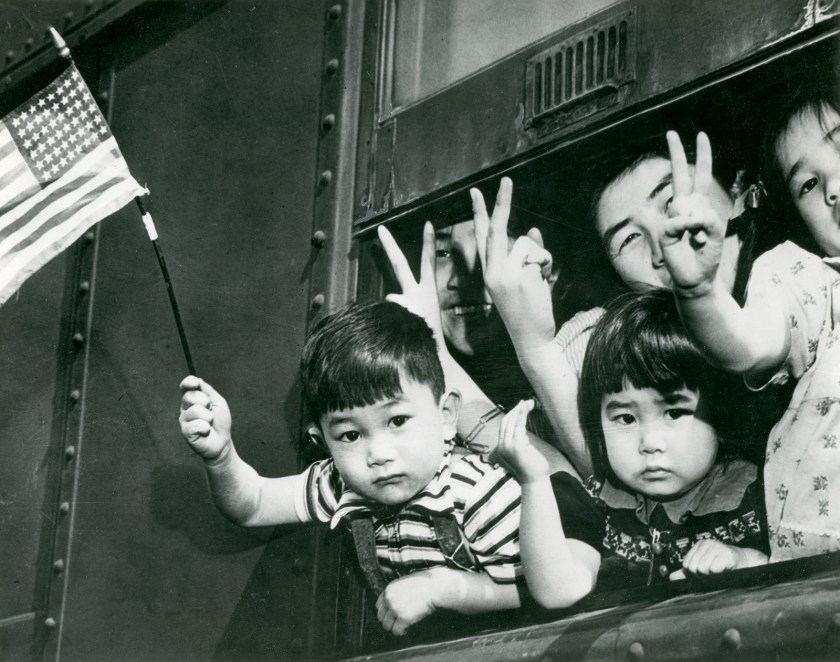
 The United States was grossly unprepared to fight a World War in 1942. The latest iteration of “War Plan Orange” (WPO-3) called for delaying tactics in the event of war with Japan, buying time to gather US Naval assets to sail for the Philippines. The problem was, there was no fleet to gather. The flower of American pacific power in the pacific, lay at the bottom of Pearl Harbor. Allied war planners turned their attention to defeating Adolf Hitler.
The United States was grossly unprepared to fight a World War in 1942. The latest iteration of “War Plan Orange” (WPO-3) called for delaying tactics in the event of war with Japan, buying time to gather US Naval assets to sail for the Philippines. The problem was, there was no fleet to gather. The flower of American pacific power in the pacific, lay at the bottom of Pearl Harbor. Allied war planners turned their attention to defeating Adolf Hitler.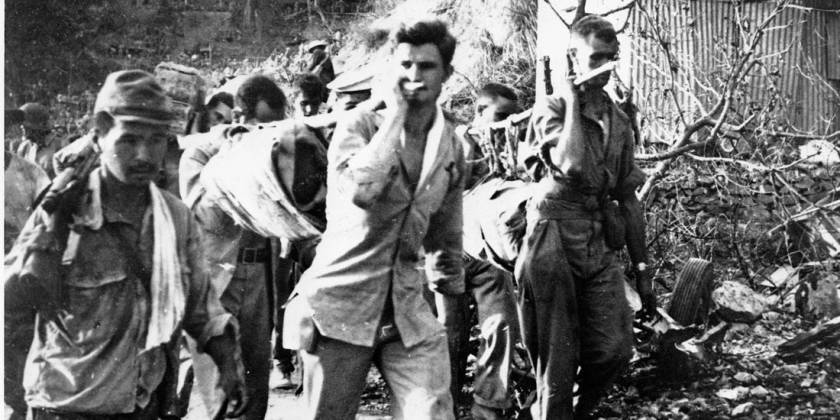 The Japanese were sadistic. Guards would beat marchers and bayonet those too weak to walk. Tormented by a thirst few among us can even imagine, men were made to stand for hours under a relentless sun, standing by a stream from which none were permitted to drink. The man who broke ranks and dove for the water was clubbed or bayoneted to death, on the spot. Japanese tanks would swerve out of their way to run over anyone who had fallen and was too slow in getting up. Some were burned alive, others buried alive. Already crippled from tropical disease and starving from the long siege of Luzon, wanton killing and savage abuse took the lives of some 500 – 650 Americans and between 5,000 – 18,000 Filipinos.
The Japanese were sadistic. Guards would beat marchers and bayonet those too weak to walk. Tormented by a thirst few among us can even imagine, men were made to stand for hours under a relentless sun, standing by a stream from which none were permitted to drink. The man who broke ranks and dove for the water was clubbed or bayoneted to death, on the spot. Japanese tanks would swerve out of their way to run over anyone who had fallen and was too slow in getting up. Some were burned alive, others buried alive. Already crippled from tropical disease and starving from the long siege of Luzon, wanton killing and savage abuse took the lives of some 500 – 650 Americans and between 5,000 – 18,000 Filipinos.  United States Marine Corps 1st Lieutenant Austin Shofner came ashore back in November, with the 4th Marines. Shofner and his fellow leathernecks engaged the Japanese as early as December 12 and received their first taste of aerial bombardment, on December 29. Promoted to Captain and placed in command of Headquarters Company, Shofner received two Silver Stars by April 15 in near-constant defense against aerial attack.
United States Marine Corps 1st Lieutenant Austin Shofner came ashore back in November, with the 4th Marines. Shofner and his fellow leathernecks engaged the Japanese as early as December 12 and received their first taste of aerial bombardment, on December 29. Promoted to Captain and placed in command of Headquarters Company, Shofner received two Silver Stars by April 15 in near-constant defense against aerial attack.
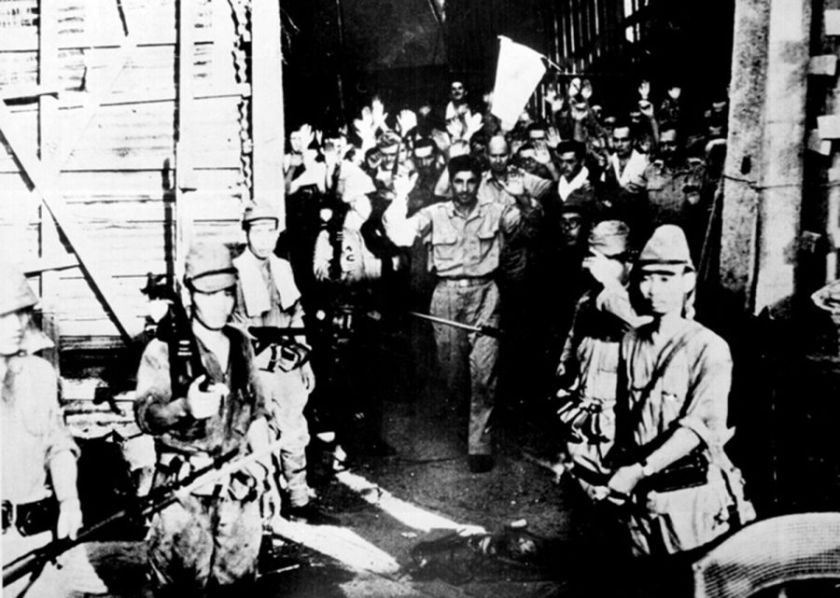 Nearly 150,000 Allied soldiers were taken captive by the Japanese Empire during World War 2. Clad in unspeakably filthy rags they were fed a mere 600 calories per day of fouled rice, supplemented only by the occasional insect or bird or rodent unlucky enough to fall into desperate hands. Diseases like malaria were all but universal as gross malnutrition led to loss of vision and unrelenting nerve pain. Dysentery, a hideously infectious disease of the large intestine reduced grown men to animated skeletons. Mere scratches resulted in grotesque tropical ulcers up to a foot in length exposing living bone and rotting flesh to swarms of ravenous insects.
Nearly 150,000 Allied soldiers were taken captive by the Japanese Empire during World War 2. Clad in unspeakably filthy rags they were fed a mere 600 calories per day of fouled rice, supplemented only by the occasional insect or bird or rodent unlucky enough to fall into desperate hands. Diseases like malaria were all but universal as gross malnutrition led to loss of vision and unrelenting nerve pain. Dysentery, a hideously infectious disease of the large intestine reduced grown men to animated skeletons. Mere scratches resulted in grotesque tropical ulcers up to a foot in length exposing living bone and rotting flesh to swarms of ravenous insects.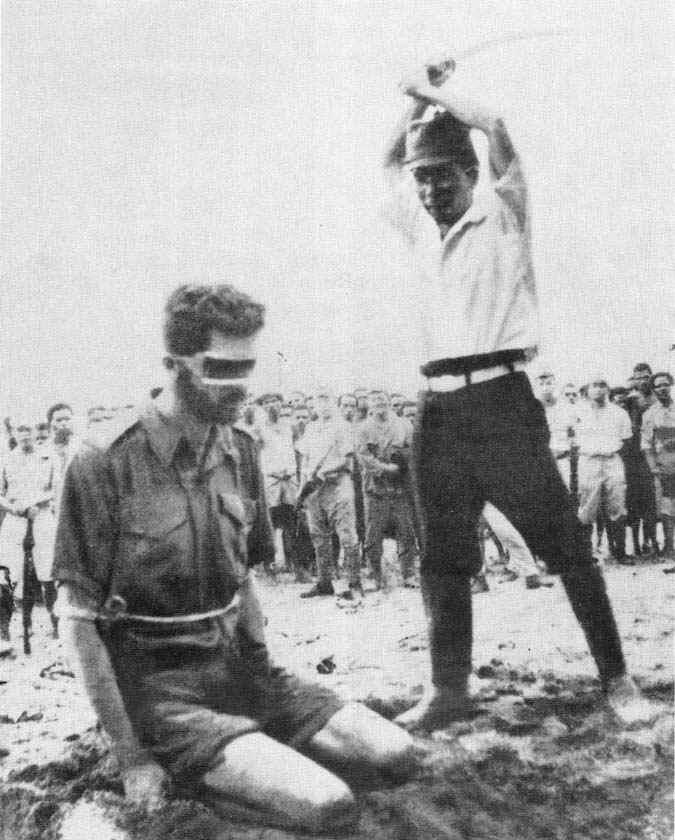 Given such cruel conditions it’s a wonder anyone escaped at all but it did happen. One time.
Given such cruel conditions it’s a wonder anyone escaped at all but it did happen. One time.















 Nineteen years ago, a news release from the Department of Defense reported “Private First Class Michael A. Arciola, 20, of Elmsford, New York, died February 15, 2005, in Al Ramadi, Iraq, from injuries sustained from enemy small arms fire. Arciola was assigned to the 1st Battalion, 503d Infantry Regiment, 2nd Infantry Division, Camp Casey, Korea”.
Nineteen years ago, a news release from the Department of Defense reported “Private First Class Michael A. Arciola, 20, of Elmsford, New York, died February 15, 2005, in Al Ramadi, Iraq, from injuries sustained from enemy small arms fire. Arciola was assigned to the 1st Battalion, 503d Infantry Regiment, 2nd Infantry Division, Camp Casey, Korea”.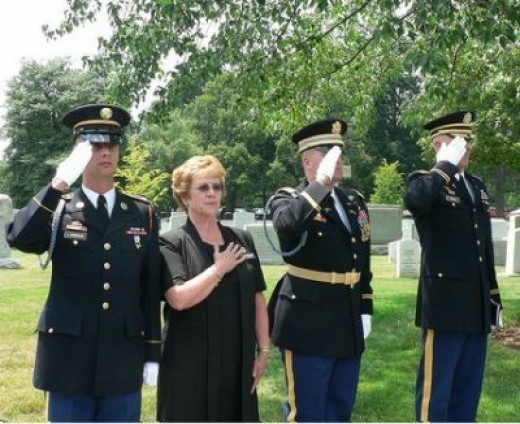
 Sometimes, a military chaplain was the only person present at these services. Both husband and wife felt that a member of the Air Force family should be present at these funerals. Before long, Gladys began to invite other officer’s wives. Over time, a group of women from the Officer’s Wives Club formed specifically for the purpose.
Sometimes, a military chaplain was the only person present at these services. Both husband and wife felt that a member of the Air Force family should be present at these funerals. Before long, Gladys began to invite other officer’s wives. Over time, a group of women from the Officer’s Wives Club formed specifically for the purpose.
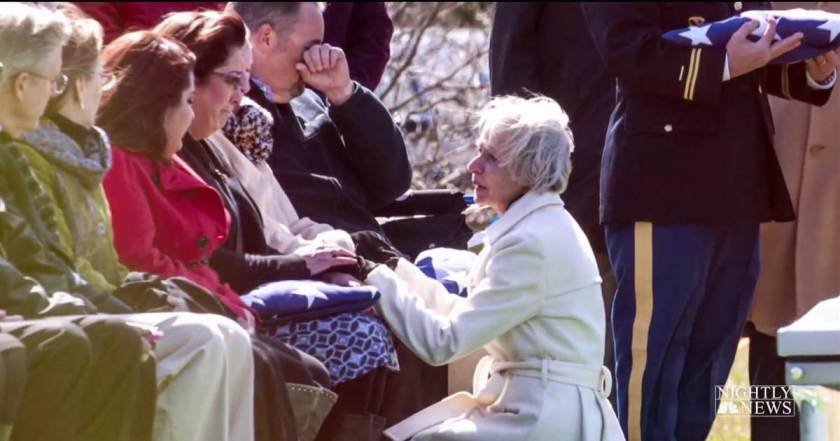
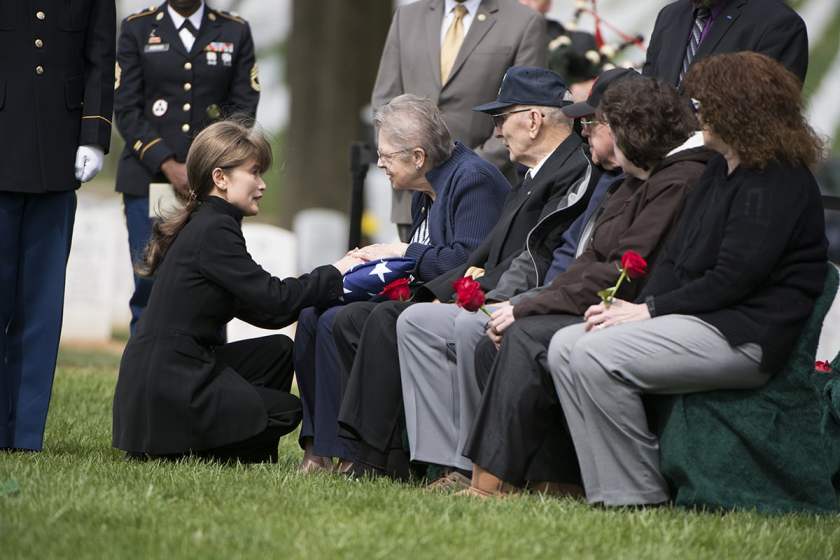
 The casual visitor cannot help but being struck with the solemnity of such an occasion. Air Force Ladies’ Chairman Sue Ellen Lansell spoke of one service where the only other guest was “one elderly gentlemen who stood at the curb and would not come to the grave site. He was from the Soldier’s Home in Washington, D. C. One soldier walked up to invite him closer, but he said no, he was not family”.
The casual visitor cannot help but being struck with the solemnity of such an occasion. Air Force Ladies’ Chairman Sue Ellen Lansell spoke of one service where the only other guest was “one elderly gentlemen who stood at the curb and would not come to the grave site. He was from the Soldier’s Home in Washington, D. C. One soldier walked up to invite him closer, but he said no, he was not family”.










You must be logged in to post a comment.