When Eddie Slovik was little, his neighbors must have considered him a bad kid. His first arrest came at the age of 12, when he and some friends were caught stealing brass from a foundry. There were other episodes between 1932 and ’37: petty theft, breaking & entering, and disturbing the peace. In 1939 he was sent to prison, for stealing a car.
 Edward Donald “Eddie” Slovik was paroled in 1942, his criminal record making him 4F. “Registrant not acceptable for military service”. He took a job at the Montella Plumbing and Heating company in Dearborn, Michigan, where he met bookkeeper Antoinette Wisniewski, the woman who would later become his wife.
Edward Donald “Eddie” Slovik was paroled in 1942, his criminal record making him 4F. “Registrant not acceptable for military service”. He took a job at the Montella Plumbing and Heating company in Dearborn, Michigan, where he met bookkeeper Antoinette Wisniewski, the woman who would later become his wife.
There they might have ridden out WWII, but the war was consuming manpower at a rate unprecedented in history. Shortly after the couple’s first anniversary, Slovik was re-classified 1A, fit for service, and drafted into the Army. Arriving in France on August 20, 1944, he was part of a 12-man replacement detachment, assigned to Company G of the 109th Infantry Regiment, US 28th Infantry Division.
Slovik and a buddy from basic training, Private John Tankey, became separated from their detachment during an artillery attack, and spent the next six weeks with Canadian MPs. It was around this time that Private Slovik decided he “wasn’t cut out for combat”.
 The rapid movement of the army during this period caused difficulty for many replacements, in finding their units. Edward Slovik and John Tankey finally caught up with the 109th on October 7. The following day, Slovik asked his company commander Captain Ralph Grotte for reassignment to a rear unit, saying he was “too scared” to be part of a rifle company. Grotte refused, confirming that, were he to run away, such an act would constitute desertion.
The rapid movement of the army during this period caused difficulty for many replacements, in finding their units. Edward Slovik and John Tankey finally caught up with the 109th on October 7. The following day, Slovik asked his company commander Captain Ralph Grotte for reassignment to a rear unit, saying he was “too scared” to be part of a rifle company. Grotte refused, confirming that, were he to run away, such an act would constitute desertion.
That, he did. Eddie Slovik deserted his unit on October 9, despite Private Tankey’s protestations that he should stay. “My mind is made up”, he said. Slovik walked several miles until he found an enlisted cook, to whom he presented the following note.
“I, Pvt. Eddie D. Slovik, 36896415, confess to the desertion of the United States Army. At the time of my desertion we were in Albuff [Elbeuf] in France. I came to Albuff as a replacement. They were shelling the town and we were told to dig in for the night. The following morning they were shelling us again. I was so scared, nerves and trembling, that at the time the other replacements moved out, I couldn’t move. I stayed there in my fox hole till it was quiet and I was able to move. I then walked into town. Not seeing any of our troops, so I stayed over night at a French hospital. The next morning I turned myself over to the Canadian Provost Corp. After being with them six weeks I was turned over to American M.P. They turned me loose. I told my commanding officer my story. I said that if I had to go out there again I’d run away. He said there was nothing he could do for me so I ran away again AND I’LL RUN AWAY AGAIN IF I HAVE TO GO OUT THERE. — Signed Pvt. Eddie D. Slovik A.S.N. 36896415”.
Slovik was repeatedly ordered to tear up the note and rejoin his unit, and there would be no consequences. Each time, he refused. The stockade didn’t scare him. He’d been in prison before, and it was better than the front lines. Beside that, he was already an ex-con. A dishonorable discharge was hardly going to change anything, in a life he expected to be filled with manual labor. “I’ve made up my mind”, he said. “I’ll take my court martial”.
Finally, instructed to write a second note on the back of the first acknowledging the legal consequences of his actions, Eddie Slovik was taken into custody.
 1.7 million courts-martial were held during WWII, 1/3rd of all the criminal cases tried in the United States during the same period. The death penalty was rarely imposed. When it was, it was almost always in cases of rape or murder.
1.7 million courts-martial were held during WWII, 1/3rd of all the criminal cases tried in the United States during the same period. The death penalty was rarely imposed. When it was, it was almost always in cases of rape or murder.
2,864 US Army personnel were tried for desertion between January 1942 and June 1948. Courts-martial handed down death sentences to 49 of them, including Eddie Slovik. Division commander Major General Norman Cota approved the sentence. “Given the situation as I knew it in November, 1944,” Cota said, “I thought it was my duty to this country to approve that sentence. If I hadn’t approved it–if I had let Slovik accomplish his purpose–I don’t know how I could have gone up to the line and looked a good soldier in the face.”
On December 9, Slovik wrote to Supreme Allied Commander Dwight D. Eisenhower, pleading for clemency. Desertion was a systemic problem at this time. Particularly after the surprise German offensive coming out of the frozen Ardennes Forest on December 16, an action that went into history as the Battle of the Bulge. Eisenhower approved the execution order on December 23, believing it to be the only way to discourage further desertions.

His uniform stripped of all insignia with an army blanket draped over his shoulders, Slovik was brought to the place of execution near the Vosges Mountains of eastern France. “They’re not shooting me for deserting the United States Army”, he said, “thousands of guys have done that. They just need to make an example out of somebody and I’m it because I’m an ex-con. I used to steal things when I was a kid, and that’s what they are shooting me for. They’re shooting me for the bread and chewing gum I stole when I was 12 years old.”
Army Chaplain Father Carl Patrick Cummings said, “Eddie, when you get up there, say a little prayer for me.” Slovik said, “Okay, Father. I’ll pray that you don’t follow me too soon”. Those were his last words. A soldier placed the black hood over his head. The execution was carried out by firing squad. It was 10:04am local time, January 31, 1945.
Edward Donald Slovik was buried in Plot E of the Oise-Aisne American Cemetery, his marker bearing a number instead of his name. Antoinette Slovik received a telegram informing her that her husband had died in the European Theater of war, and a letter instructing her to return a $55 allotment check. She would not learn about the execution for nine years.

In 1987, President Ronald Reagan ordered the repatriation of Slovik’s remains. He was re-interred at Detroit’s Woodmere Cemetery next to Antoinette, who had gone to her final rest eight years earlier.
In all theaters of WWII, the United States military executed 102 of its own, almost always for the unprovoked rape and/or murder of civilians. From the Civil War to this day, Eddie Slovik’s death sentence remains the only one ever carried out for the crime of desertion. At least one member of the tribunal which condemned him to death, would come to see it as a miscarriage of justice.
Nick Gozik of Pittsburg passed away in 2015, at the age of 95. He was there in 1945, a fellow soldier called to witness the execution. “Justice or legal murder”, he said, “I don’t know, but I want you to know I think he was the bravest man in that courtyard that day…All I could see was a young soldier, blond-haired, walking as straight as a soldier ever walked. I thought he was the bravest soldier I ever saw.”




 “I beg to ask the steps of that process”, asked the student. Confucius replied, “Look not at what is contrary to propriety. Listen not to what is contrary to propriety. Speak not what is contrary to propriety. Make no movement which is contrary to propriety”.
“I beg to ask the steps of that process”, asked the student. Confucius replied, “Look not at what is contrary to propriety. Listen not to what is contrary to propriety. Speak not what is contrary to propriety. Make no movement which is contrary to propriety”.
 The visual play on words, then, depicts Iwazaru covering his mouth, Kikazaru covering his ears, and Mizaru covering his eyes.
The visual play on words, then, depicts Iwazaru covering his mouth, Kikazaru covering his ears, and Mizaru covering his eyes.



 When Nazi Germany invaded Poland the following September, London mayor Herbert Morrison was at 10 Downing Street, meeting with Chamberlain’s aide, Sir Horace Wilson. Morrison believed that the time had come for Operation Pied Piper. A year to the day from the Prime Minister’s “Peace in our Time” declaration, Wilson protested. “But we’re not at war yet, and we wouldn’t want to do anything to upset delicate negotiations, would we?”
When Nazi Germany invaded Poland the following September, London mayor Herbert Morrison was at 10 Downing Street, meeting with Chamberlain’s aide, Sir Horace Wilson. Morrison believed that the time had come for Operation Pied Piper. A year to the day from the Prime Minister’s “Peace in our Time” declaration, Wilson protested. “But we’re not at war yet, and we wouldn’t want to do anything to upset delicate negotiations, would we?”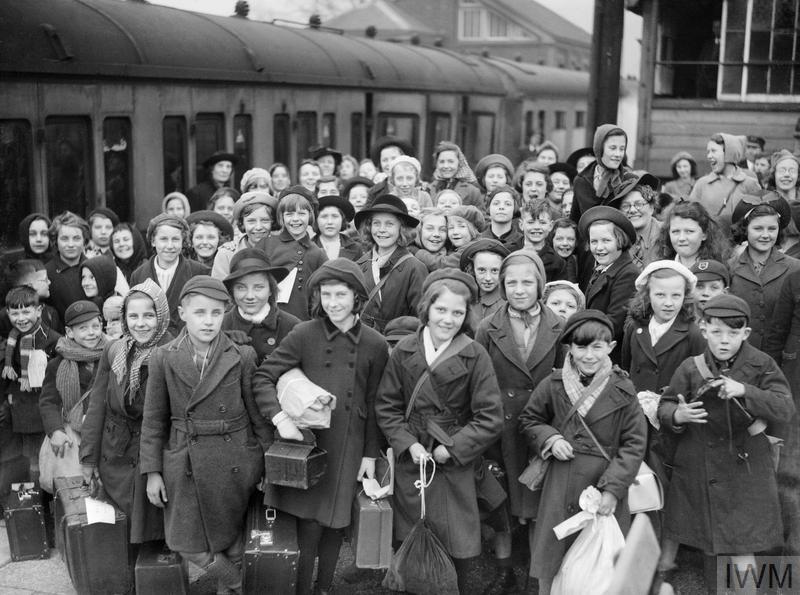
 BBC History reported that, “within a week, a quarter of the population of Britain would have a new address”.
BBC History reported that, “within a week, a quarter of the population of Britain would have a new address”. The evacuation of all that humanity ran relatively smoothly, considering. James Roffey, founder of the Evacuees Reunion Association, recalls ‘We marched to Waterloo Station behind our head teacher carrying a banner with our school’s name on it. We all thought it was a holiday, but the only thing we couldn’t work out was why the women and girls were crying.’
The evacuation of all that humanity ran relatively smoothly, considering. James Roffey, founder of the Evacuees Reunion Association, recalls ‘We marched to Waterloo Station behind our head teacher carrying a banner with our school’s name on it. We all thought it was a holiday, but the only thing we couldn’t work out was why the women and girls were crying.’ In the 2003 BBC Radio documentary “Evacuation: The True Story,” clinical psychologist Steve Davis described the worst cases, as “little more than a pedophile’s charter.”
In the 2003 BBC Radio documentary “Evacuation: The True Story,” clinical psychologist Steve Davis described the worst cases, as “little more than a pedophile’s charter.” Authorities produced posters urging parents to leave the kids where they were, and a good thing, too. The Blitz against London itself began on September 7. The city experienced the most devastating attack to-date on December 29, in a blanket fire-bombing that killed almost 3,600 civilians.
Authorities produced posters urging parents to leave the kids where they were, and a good thing, too. The Blitz against London itself began on September 7. The city experienced the most devastating attack to-date on December 29, in a blanket fire-bombing that killed almost 3,600 civilians. By October 1940, the “
By October 1940, the “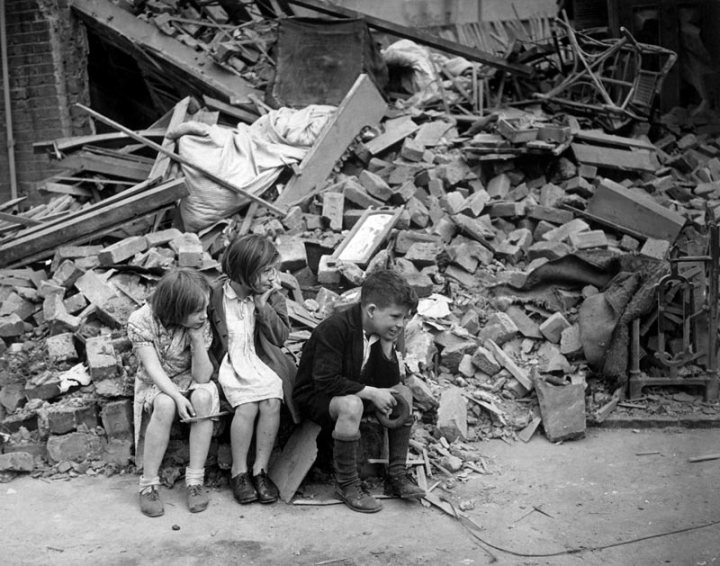
 In the end, many family ‘reunions’ were as emotionally bruising as the original breakup. Years had come and gone and new relationships had formed. The war had turned biological family members, into all but strangers.
In the end, many family ‘reunions’ were as emotionally bruising as the original breakup. Years had come and gone and new relationships had formed. The war had turned biological family members, into all but strangers.

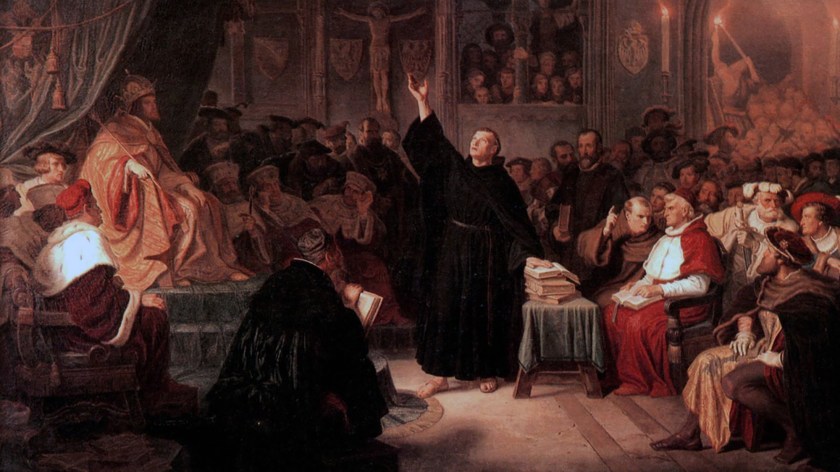
 Martin Luther wrote to Archbishop Albrecht on October 31, 1517, objecting to this sale of indulgences. He enclosed a copy of his “Disputation of Martin Luther on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences”, a document which came to be known as his “95 Theses”.
Martin Luther wrote to Archbishop Albrecht on October 31, 1517, objecting to this sale of indulgences. He enclosed a copy of his “Disputation of Martin Luther on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences”, a document which came to be known as his “95 Theses”.





 20,000 died from sickness or hunger, or were murdered by Japanese guards on the 60 mile “death march” from Bataan, into captivity at Cabanatuan prison and others.
20,000 died from sickness or hunger, or were murdered by Japanese guards on the 60 mile “death march” from Bataan, into captivity at Cabanatuan prison and others. Two rice rations per day, fewer than 800 calories, were supplemented by the occasional animal or insect caught and killed inside camp walls, or by the rare food items smuggled in by civilian visitors.
Two rice rations per day, fewer than 800 calories, were supplemented by the occasional animal or insect caught and killed inside camp walls, or by the rare food items smuggled in by civilian visitors. On December 14, some fifty to sixty soldiers of the Japanese 14th Area Army in Palawan doused 150 prisoners with gasoline and set them on fire, machine gunning or clubbing any who tried to escape the flames. Some thirty to forty managed to escape the killing zone, only to be hunted down and murdered, one by one. Eleven managed to escape the slaughter, and lived to tell the tale. 139 were burned, clubbed or machine gunned to death.
On December 14, some fifty to sixty soldiers of the Japanese 14th Area Army in Palawan doused 150 prisoners with gasoline and set them on fire, machine gunning or clubbing any who tried to escape the flames. Some thirty to forty managed to escape the killing zone, only to be hunted down and murdered, one by one. Eleven managed to escape the slaughter, and lived to tell the tale. 139 were burned, clubbed or machine gunned to death.


 He dressed and shaved, put on his best clothes, and walked out of camp. Passing guerrillas found him and passed him to a tank destroyer. Give the man points for style. A few days later, Edwin Rose strolled into 6th army headquarters, a cane tucked under his arm.
He dressed and shaved, put on his best clothes, and walked out of camp. Passing guerrillas found him and passed him to a tank destroyer. Give the man points for style. A few days later, Edwin Rose strolled into 6th army headquarters, a cane tucked under his arm.
 Murphy’s company commander thought he wasn’t big enough for infantry service, and attempted to transfer him to cook and bakers’ school. Murphy refused. He wanted to be a combat soldier.
Murphy’s company commander thought he wasn’t big enough for infantry service, and attempted to transfer him to cook and bakers’ school. Murphy refused. He wanted to be a combat soldier. He was still in the hospital when his unit moved into the Vosges Mountains, in Eastern France.
He was still in the hospital when his unit moved into the Vosges Mountains, in Eastern France. “Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”.
“Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”. The man who had once been judged too small to fight was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers of WW2, having received every military combat award for valor the United States Army has to give, plus additional awards for heroism, from France and from Belgium.
The man who had once been judged too small to fight was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers of WW2, having received every military combat award for valor the United States Army has to give, plus additional awards for heroism, from France and from Belgium.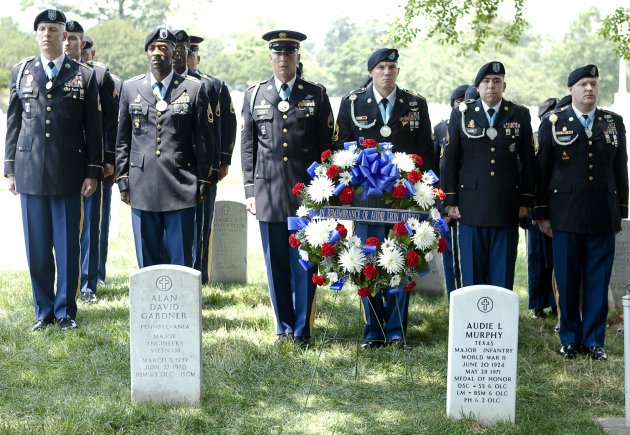


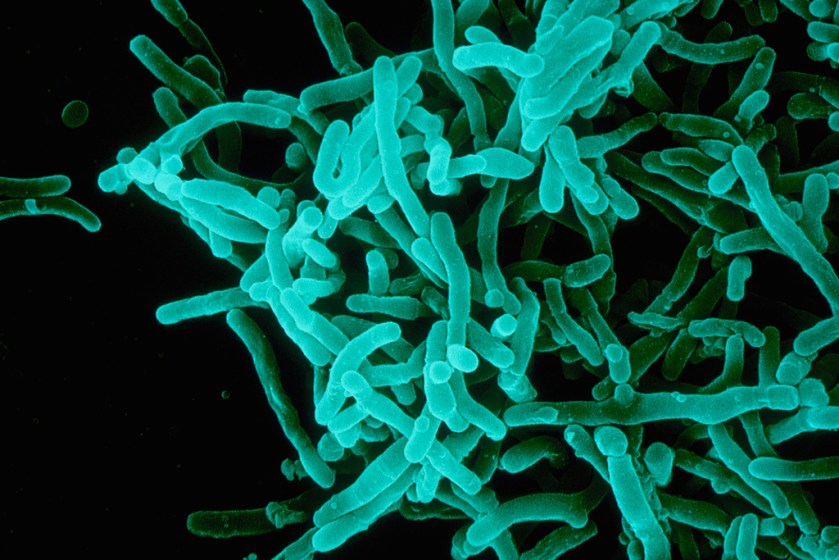
 Dr. Curtis Welch practiced medicine in Nome, Alaska, in 1925. Several children became ill with what he first diagnosed as tonsillitis. More came down with sore throats, early sufferers beginning to die as Welch observed the pseudomembrane of diphtheria. He had ordered fresh antitoxin the year before, but the shipment hadn’t arrived by the time the ports froze over. By January, all the serum in Nome was expired.
Dr. Curtis Welch practiced medicine in Nome, Alaska, in 1925. Several children became ill with what he first diagnosed as tonsillitis. More came down with sore throats, early sufferers beginning to die as Welch observed the pseudomembrane of diphtheria. He had ordered fresh antitoxin the year before, but the shipment hadn’t arrived by the time the ports froze over. By January, all the serum in Nome was expired.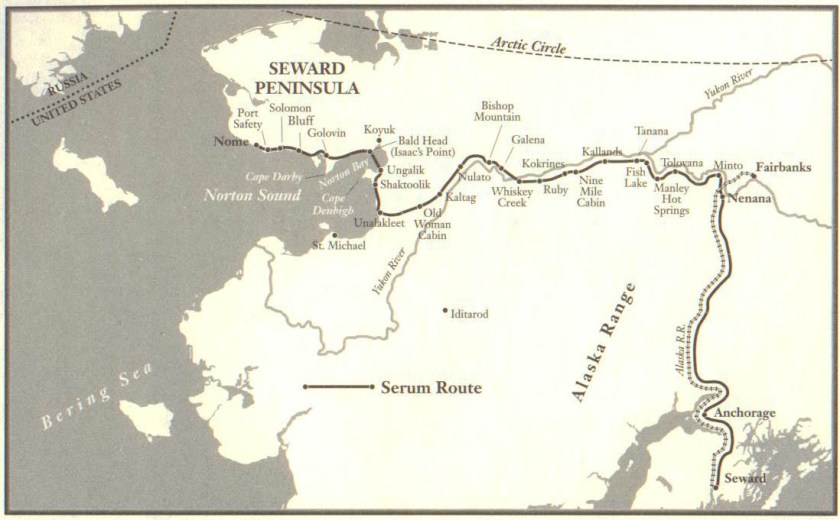
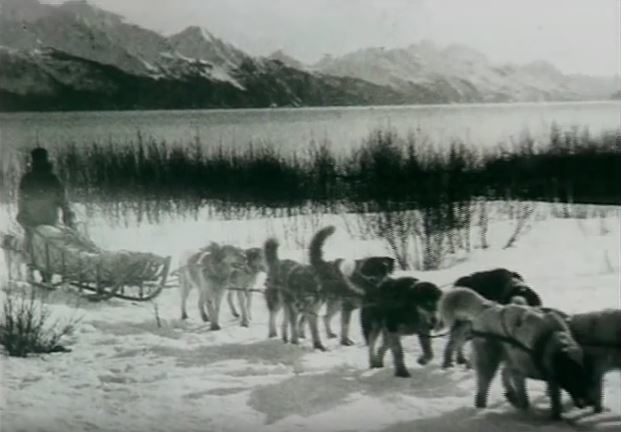


 20 mushers and 150 dogs or more had covered 674 miles in 5 days, 7½ hours, a distance that normally took the mail relay 2-3 weeks. Not a single serum ampule was broken.
20 mushers and 150 dogs or more had covered 674 miles in 5 days, 7½ hours, a distance that normally took the mail relay 2-3 weeks. Not a single serum ampule was broken.


 The Continental Congress appointed George Washington General of this “Army” on June 15, two days before the British assault on Farmer Breed’s hill. An action which took its name from that of a neighboring farmer, going into history as the Battle of Bunker Hill.
The Continental Congress appointed George Washington General of this “Army” on June 15, two days before the British assault on Farmer Breed’s hill. An action which took its name from that of a neighboring farmer, going into history as the Battle of Bunker Hill.


 The first military burial, but not the first. When Private Christman went to his rest in our nation’s most hallowed ground, his grave joined that of Mary Randolph, buried some thirty-six years earlier.
The first military burial, but not the first. When Private Christman went to his rest in our nation’s most hallowed ground, his grave joined that of Mary Randolph, buried some thirty-six years earlier. Mary Randolph, Pocahontas’ direct descendant and cousin to Thomas Jefferson, was the cousin of George Washington Parke Custis, adopted step-grandson of George Washington, and the godmother of Custis’ daughter, Mary Anna Randolph Custis, wife of Robert E. Lee.
Mary Randolph, Pocahontas’ direct descendant and cousin to Thomas Jefferson, was the cousin of George Washington Parke Custis, adopted step-grandson of George Washington, and the godmother of Custis’ daughter, Mary Anna Randolph Custis, wife of Robert E. Lee. Mary Randolph is best known as the author of America’s first regional cookbook, “The Virginia Housewife”. The Virginia Culinary Thymes writes that “It is interesting to note that all the cookery at that time was done in kitchens that had changed little over the centuries. In Virginia, the kitchen was typically a separate building for reasons of safety, summer heat and the smells from the kitchen. The heart of the kitchen was a large fireplace where meat was roasted and cauldrons of water and broth simmered most of the day. Swinging cranes and various devices made to control temperature and the cooking processes were used. The Dutch oven and the chafing dish were found in most kitchens. The brick oven used for baking was located next to the fireplace. A salamander was used to move baked products around in the oven and it could also be heated and held over food for browning“.
Mary Randolph is best known as the author of America’s first regional cookbook, “The Virginia Housewife”. The Virginia Culinary Thymes writes that “It is interesting to note that all the cookery at that time was done in kitchens that had changed little over the centuries. In Virginia, the kitchen was typically a separate building for reasons of safety, summer heat and the smells from the kitchen. The heart of the kitchen was a large fireplace where meat was roasted and cauldrons of water and broth simmered most of the day. Swinging cranes and various devices made to control temperature and the cooking processes were used. The Dutch oven and the chafing dish were found in most kitchens. The brick oven used for baking was located next to the fireplace. A salamander was used to move baked products around in the oven and it could also be heated and held over food for browning“. Mrs. Randolph was an early advocate of the now-common use of herbs, spices and wines in cooking. Her recipe for apple fritters calls for slices of apple marinated in a combination of brandy, white wine, sugar, cinnamon, and lemon rind.
Mrs. Randolph was an early advocate of the now-common use of herbs, spices and wines in cooking. Her recipe for apple fritters calls for slices of apple marinated in a combination of brandy, white wine, sugar, cinnamon, and lemon rind.
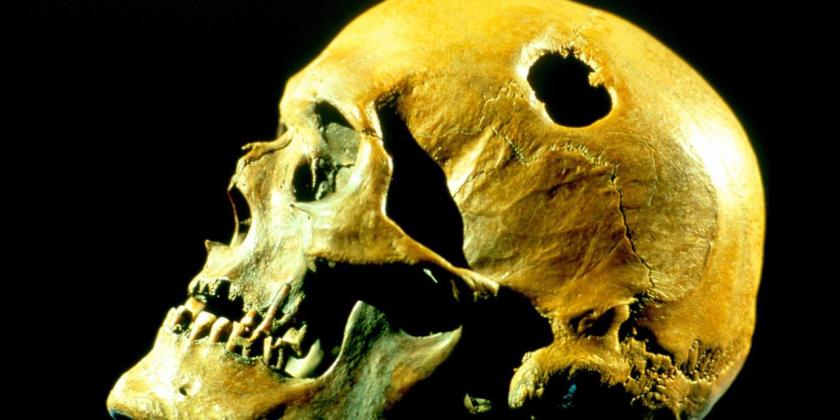

 To prove the value of his ‘third eye’ theory, to his own satisfaction if to no one else, Hughes drilled a hole in his own skull in 1965, using a Black & Decker electric drill. He must have thought it proved the point, because he expanded on his theory with “Trepanation: A Cure for Psychosis”, followed by an autobiography, “The Book with the Hole”, published in 1972.
To prove the value of his ‘third eye’ theory, to his own satisfaction if to no one else, Hughes drilled a hole in his own skull in 1965, using a Black & Decker electric drill. He must have thought it proved the point, because he expanded on his theory with “Trepanation: A Cure for Psychosis”, followed by an autobiography, “The Book with the Hole”, published in 1972. At age 27, Amanda Feilding brought an electric dentist’s drill to her London apartment, and drilled a hole in her skull. After four unsuccessful years trying to find a surgeon to do it for her, “I thought, ‘Well, I’m a sculptor, I may as well do it myself'”.
At age 27, Amanda Feilding brought an electric dentist’s drill to her London apartment, and drilled a hole in her skull. After four unsuccessful years trying to find a surgeon to do it for her, “I thought, ‘Well, I’m a sculptor, I may as well do it myself'”. At the time, the Iron County DA also considered charges against ABC News reporter Chris Cuomo, for aiding in the crime.
At the time, the Iron County DA also considered charges against ABC News reporter Chris Cuomo, for aiding in the crime.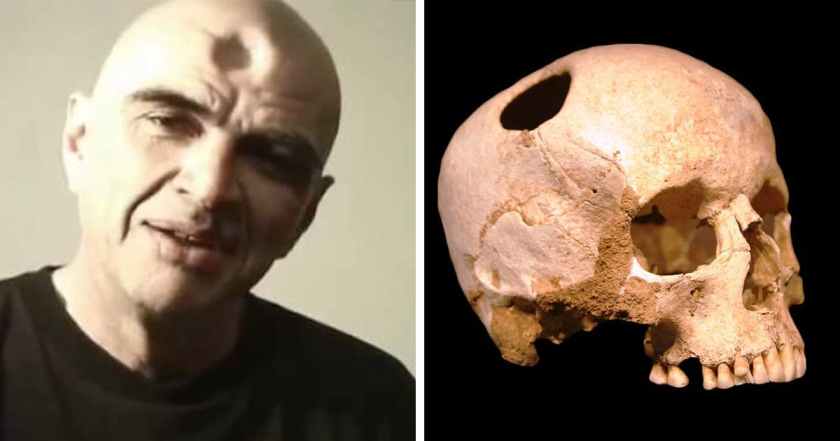
You must be logged in to post a comment.