Emil Joseph Kapaun was the son of Czech immigrants, a farm kid who grew up in 1920s Kansas. Graduating from Pilsen High, class of 1930, he spent much of the 30s in theological seminary, becoming an ordained priest of the Roman Catholic faith on June 9, 1940.
 Kapaun served as military chaplain toward the end of WWII, before leaving the army in 1946, and rejoining in 1948.
Kapaun served as military chaplain toward the end of WWII, before leaving the army in 1946, and rejoining in 1948.
Father Kapaun was ordered to Korea a month after the North invaded the South, joining the 8th Cavalry Regiment of the 1st Cavalry Division, out of Fort Bliss.
His unit entered combat at the Pusan perimeter, moving steadily northward through the summer and fall of 1950. Kapaun would minister to the dead and dying, performing baptisms, hearing first confessions, offering Holy Communion and celebrating Mass from an improvised altar set up on the hood of a jeep.
Kapaun once lost his Mass kit to enemy fire. He earned a Bronze Star in September that year, when he ran through intense enemy fire to rescue a wounded soldier. His was no rear-echelon ministry.

A single regiment was attacked by the 39th Chinese Corps on November 1, and completely overrun the following day. For the 8th Cav., the battle of Unsan was one of the most devastating defeats of the Korean War. Father Kapaun was ordered to evade, an order he defied. He was performing last rites for a dying soldier, when he was seized by Chinese communist forces.
Prisoners were force marched 87 miles to a Communist POW camp near Pyoktong, in North Korea. Conditions in the camp were gruesome. 1st Lt. Michael Dowe was among the prisoners, it’s through him that we know much of what happened there. Dowe later described Father Kapaun trading his watch for a blanket, only to cut it up to fashion socks for the feet of fellow prisoners.
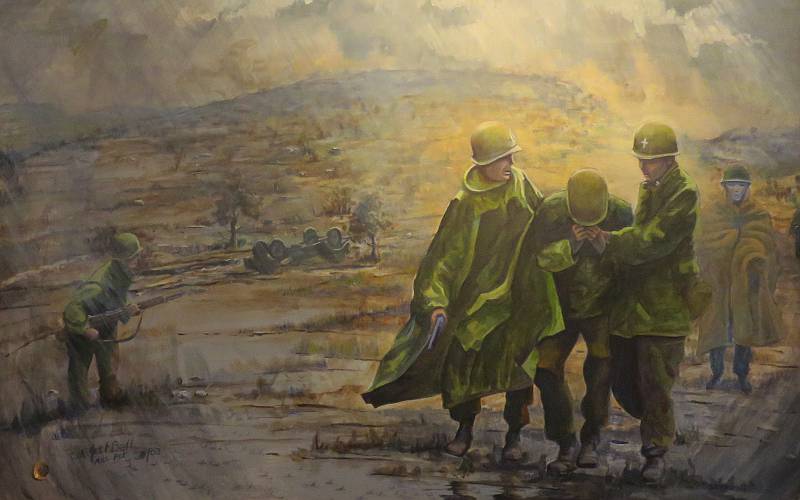

Father Kapaun would risk his life, sneaking into the fields around the prison compound to look for something to eat. He would always bring it back to the communal pot.
Chinese Communist guards would taunt him during daily indoctrination sessions, “Where is your god now?” Before and after these sessions, he would move through the camp, ministering to Catholic and non-Catholic alike. Kapaun would slip in behind every work detail, cleaning latrines while other prisoners argued over who’d get the job. He’d wash the filthy laundry of those made weak and incontinent with dysentery.
 Starving, suffering from a blood clot in his leg and a severe eye infection, Father Kapaun led Easter services in April, 1951. He was incapacitated a short time later. Chinese guards carried him off to a “hospital” – a fetid, stinking part of the camp known to prisoners as the “Death House”, from which few ever returned. “If I don’t come back”, he said, “tell my Bishop that I died a happy death.”
Starving, suffering from a blood clot in his leg and a severe eye infection, Father Kapaun led Easter services in April, 1951. He was incapacitated a short time later. Chinese guards carried him off to a “hospital” – a fetid, stinking part of the camp known to prisoners as the “Death House”, from which few ever returned. “If I don’t come back”, he said, “tell my Bishop that I died a happy death.”
In the end, Father Kapaun was too weak to lift the plate holding the meager ration the guards had left for him. US Army records report that Fr. Kapaun died of pneumonia on May 6, 1951.
His fellow prisoners will tell you that he died on the 23rd, of malnutrition and starvation. He was 35.
Scores of men credit their survival to Chaplain Kapaun. In 2013, President Barack Obama presented Kapaun’s family with the Medal of Honor, posthumous, for his heroism at Unsan. The New York Times reported that April, “The chaplain “calmly walked through withering enemy fire” and hand-to-hand combat to provide medical aid, comforting words or the last rites of the Roman Catholic Church to the wounded, the citation said. When he saw a Chinese soldier about to execute a wounded comrade, Sgt. First Class Herbert A. Miller, he rushed to push the gun away. Mr. Miller, now 88, was at the White House for the ceremony with other veterans, former prisoners of war and members of the Kapaun family”.
 Pope John Paul II named Father Kapaun a “Servant of God” in 1993, the first step toward Roman Catholic Sainthood. On November 9, 2015, the Catholic Diocese of Wichita submitted a 1,066 page report on the life of Chaplain Kapaun, to the Roman Curia at the Vatican. A team of six historians reviewed the case for beatification. On June 21, 2016, the committee unanimously approved the petition. At the time I write this, Father Emil Joseph Kapaun’s supporters continue working to have him declared a Saint of the Roman Catholic Church, for his lifesaving ministrations at Pyoktong.
Pope John Paul II named Father Kapaun a “Servant of God” in 1993, the first step toward Roman Catholic Sainthood. On November 9, 2015, the Catholic Diocese of Wichita submitted a 1,066 page report on the life of Chaplain Kapaun, to the Roman Curia at the Vatican. A team of six historians reviewed the case for beatification. On June 21, 2016, the committee unanimously approved the petition. At the time I write this, Father Emil Joseph Kapaun’s supporters continue working to have him declared a Saint of the Roman Catholic Church, for his lifesaving ministrations at Pyoktong.




 Murphy’s company commander thought he wasn’t big enough for infantry service, and attempted to transfer him to cook and bakers’ school. Murphy refused. He wanted to be a combat soldier.
Murphy’s company commander thought he wasn’t big enough for infantry service, and attempted to transfer him to cook and bakers’ school. Murphy refused. He wanted to be a combat soldier. He was still in the hospital when his unit moved into the Vosges Mountains, in Eastern France.
He was still in the hospital when his unit moved into the Vosges Mountains, in Eastern France. “Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”.
“Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”. The man who had once been judged too small to fight was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers of WW2, having received every military combat award for valor the United States Army has to give, plus additional awards for heroism, from France and from Belgium.
The man who had once been judged too small to fight was one of the most decorated American combat soldiers of WW2, having received every military combat award for valor the United States Army has to give, plus additional awards for heroism, from France and from Belgium.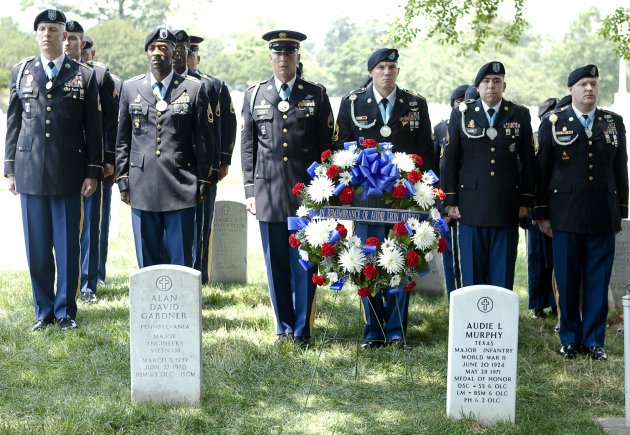


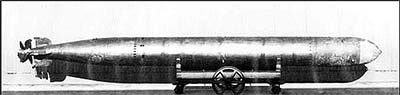 Among the Mark-XIV’s more pronounced deficiencies was a tendency to run about 10-ft. too deep, causing it to miss with depressing regularity. The magnetic exploder often caused premature firing of the warhead, and the contact exploder frequently failed altogether. There must be no worse sound to a submariner, than the metallic ‘clink’ of a dud torpedo bouncing off an enemy hull.
Among the Mark-XIV’s more pronounced deficiencies was a tendency to run about 10-ft. too deep, causing it to miss with depressing regularity. The magnetic exploder often caused premature firing of the warhead, and the contact exploder frequently failed altogether. There must be no worse sound to a submariner, than the metallic ‘clink’ of a dud torpedo bouncing off an enemy hull.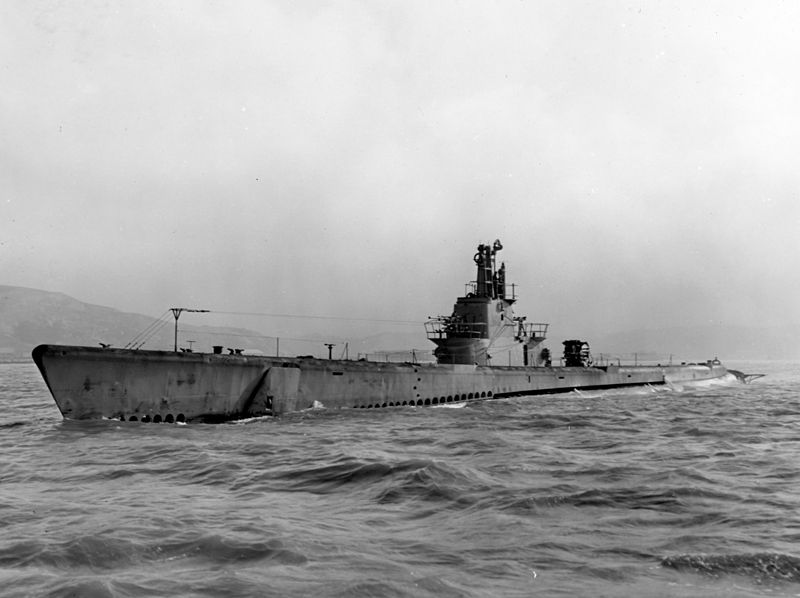
 Sam Moses, writing for historynet’s “Hell and High Water,” writes, “In five war patrols between May 1944 and August 1945, the 1,500-ton Barb sank twenty-nine ships and destroyed numerous factories using shore bombardment and rockets launched from the foredeck”.
Sam Moses, writing for historynet’s “Hell and High Water,” writes, “In five war patrols between May 1944 and August 1945, the 1,500-ton Barb sank twenty-nine ships and destroyed numerous factories using shore bombardment and rockets launched from the foredeck”. Two weeks later, USS Barb spotted a 30-ship convoy, anchored in three parallel lines in Namkwan Harbor, on the China coast. Slipping past the Japanese escort guarding the harbor entrance under cover of darkness, the American submarine crept to within 3,000 yards.
Two weeks later, USS Barb spotted a 30-ship convoy, anchored in three parallel lines in Namkwan Harbor, on the China coast. Slipping past the Japanese escort guarding the harbor entrance under cover of darkness, the American submarine crept to within 3,000 yards. On completion of her 11th patrol, USS Barb underwent overhaul and alterations, including the installation of 5″ rocket launchers, setting out on her 12th and final patrol in early June.
On completion of her 11th patrol, USS Barb underwent overhaul and alterations, including the installation of 5″ rocket launchers, setting out on her 12th and final patrol in early June. Working so close to a Japanese guard tower that they could almost hear the snoring of the sentry, the eight-man team dug into the space between two ties and buried the 55-pound scuttling charge. They then dug into the space between the next two ties, and placed the battery.
Working so close to a Japanese guard tower that they could almost hear the snoring of the sentry, the eight-man team dug into the space between two ties and buried the 55-pound scuttling charge. They then dug into the space between the next two ties, and placed the battery.

 A “Fidelity Medallion” was awarded to three militia men in 1780, for the capture of
A “Fidelity Medallion” was awarded to three militia men in 1780, for the capture of  An Army version of the medal was created the following July, first awarded to six Union soldiers for hijacking the Confederate locomotive, “The General”. Leader of the raid James Andrews was caught and hanged as a Union spy. He alone was judged ineligible for the medal of honor, as he was a civilian.
An Army version of the medal was created the following July, first awarded to six Union soldiers for hijacking the Confederate locomotive, “The General”. Leader of the raid James Andrews was caught and hanged as a Union spy. He alone was judged ineligible for the medal of honor, as he was a civilian. Few soldiers on the Civil War battlefield had a quicker route to death’s door, than the color bearer. National and regimental flags were all-important sources of inspiration and communication.
Few soldiers on the Civil War battlefield had a quicker route to death’s door, than the color bearer. National and regimental flags were all-important sources of inspiration and communication.


 Father
Father 
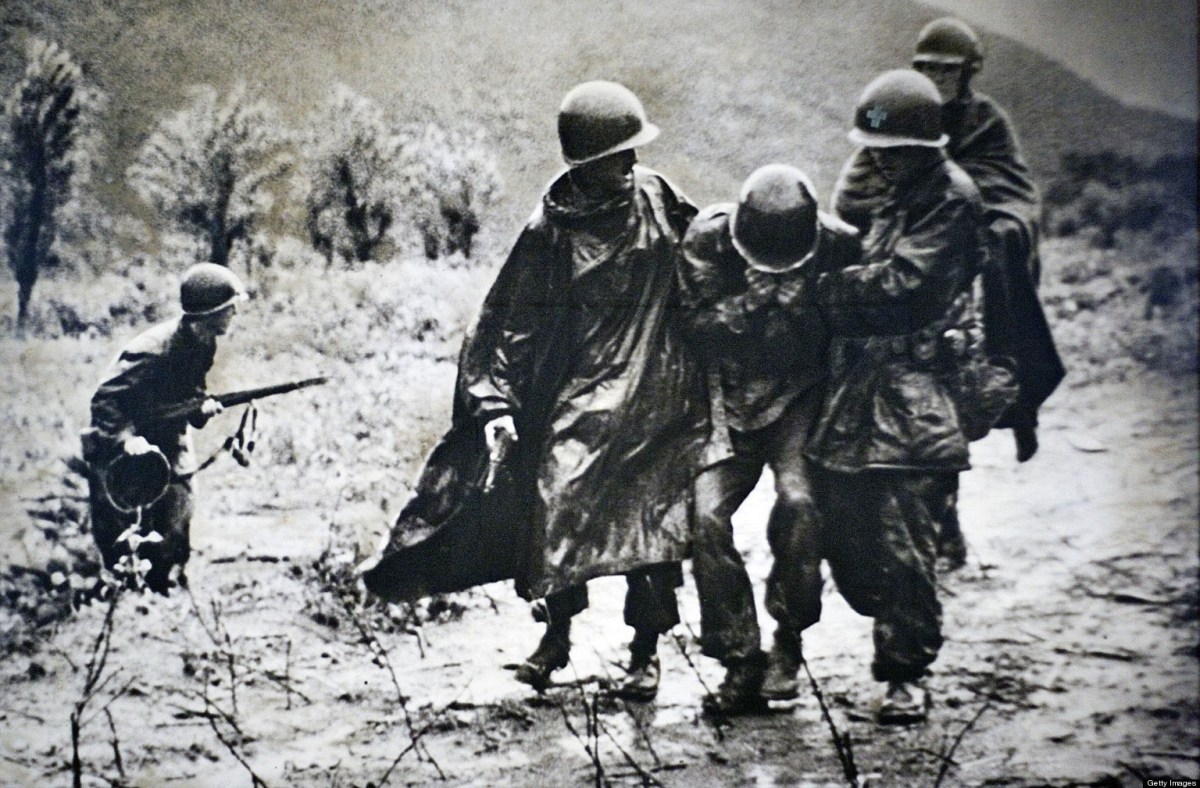




 Emil Joseph Kapaun was the son of Czech immigrants, a farm kid who grew up in 1920s Kansas. Graduating from Pilsen High, class of 1930, Kapaun spent much of the 30s in theological seminary, becoming an ordained priest of the Roman Catholic faith on June 9, 1940.
Emil Joseph Kapaun was the son of Czech immigrants, a farm kid who grew up in 1920s Kansas. Graduating from Pilsen High, class of 1930, Kapaun spent much of the 30s in theological seminary, becoming an ordained priest of the Roman Catholic faith on June 9, 1940.
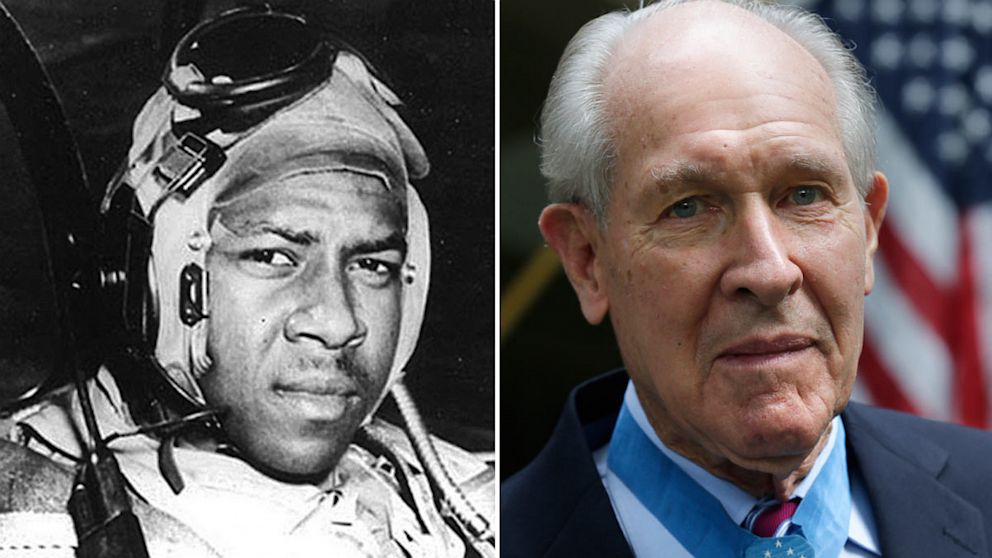







 Hudner pleaded with authorities the following day to go back to the crash site, but they were unwilling to risk further loss of life. They would napalm the crash site so that the Chinese couldn’t get to the aircraft or the body, though pilots reported that it looked like the Brown’s body had already been disturbed.
Hudner pleaded with authorities the following day to go back to the crash site, but they were unwilling to risk further loss of life. They would napalm the crash site so that the Chinese couldn’t get to the aircraft or the body, though pilots reported that it looked like the Brown’s body had already been disturbed.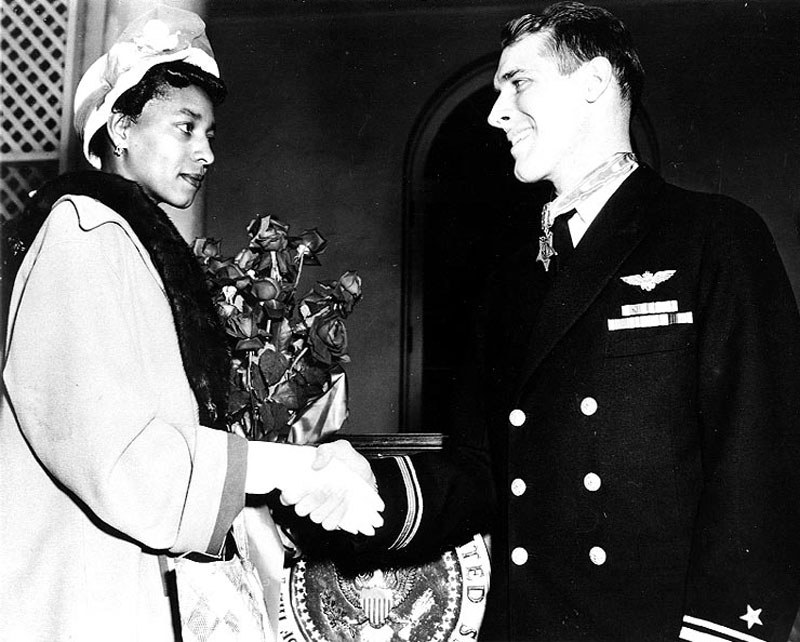







 Joining the 3rd Infantry Division of George S. Patton’s 7th Army, Murphy participated in amphibious landings in Sicily in July, fighting in nearly every aspect of the Italian campaign. From Palermo to Messina and on to Naples, Anzio and Rome, the Germans were driven out of the Italian peninsula in savage and near continuous fighting that killed a member of my own family. By mid-December, the 3rd ID suffered 683 dead, 170 missing, and 2,412 wounded. Now Sergeant Murphy was there for most of it, excepting two periods when he was down with malaria.
Joining the 3rd Infantry Division of George S. Patton’s 7th Army, Murphy participated in amphibious landings in Sicily in July, fighting in nearly every aspect of the Italian campaign. From Palermo to Messina and on to Naples, Anzio and Rome, the Germans were driven out of the Italian peninsula in savage and near continuous fighting that killed a member of my own family. By mid-December, the 3rd ID suffered 683 dead, 170 missing, and 2,412 wounded. Now Sergeant Murphy was there for most of it, excepting two periods when he was down with malaria. “Colmar Pocket” was an 850 square mile area held by German troops: Murphy described it as “a huge and dangerous bridgehead thrusting west of the Rhine like an iron fist. Fed with men and materiel from across the river, it is a constant threat to our right flank; and potentially it is a perfect springboard from which the enemy could start a powerful counterattack.”
“Colmar Pocket” was an 850 square mile area held by German troops: Murphy described it as “a huge and dangerous bridgehead thrusting west of the Rhine like an iron fist. Fed with men and materiel from across the river, it is a constant threat to our right flank; and potentially it is a perfect springboard from which the enemy could start a powerful counterattack.” Let Murphy’s Medal of Honor Citation describe what happened next: “Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”.
Let Murphy’s Medal of Honor Citation describe what happened next: “Second Lieutenant Audie L. Murphy, 01692509, 15th Infantry, Army of the United States, on 26 January 1945, near Holtzwihr, France, commanded Company B, which was attacked by six tanks and waves of infantry. Lieutenant Murphy ordered his men to withdraw to a prepared position in a woods while he remained forward at his command post and continued to give fire directions to the artillery by telephone. Behind him to his right one of our tank destroyers received a direct hit and began to burn. Its crew withdrew to the woods. Lieutenant Murphy continued to direct artillery fire which killed large numbers of the advancing enemy infantry. With the enemy tanks abreast of his position, Lieutenant Murphy climbed on the burning tank destroyer which was in danger of blowing up any instant and employed its .50 caliber machine gun against the enemy. He was alone and exposed to the German fire from three sides, but his deadly fire killed dozens of Germans and caused their infantry attack to waver. The enemy tanks, losing infantry support, began to fall back. For an hour the Germans tried every available weapon to eliminate Lieutenant Murphy, but he continued to hold his position and wiped out a squad which was trying to creep up unnoticed on his right flank. Germans reached as close as 10 yards only to be mowed down by his fire. He received a leg wound but ignored it and continued the single-handed fight until his ammunition was exhausted. He then made his way to his company, refused medical attention, and organized the company in a counterattack which forced the Germans to withdraw. His directing of artillery fire wiped out many of the enemy; he personally killed or wounded about 50. Lieutenant Murphy’s indomitable courage and his refusal to give an inch of ground saved his company from possible encirclement and destruction and enabled it to hold the woods which had been the enemy’s objective”. Hollywood and, until his death in a plane crash in 1971, his post-war life was never free of it.
Hollywood and, until his death in a plane crash in 1971, his post-war life was never free of it.
You must be logged in to post a comment.