When the Great Depression fell over the nation in the 1930s, few states had a harder time of it, than Oklahoma. Loyce Edward Deen grew up in this world, the seventh of eight children born to Grace and Allen Deen in the small town of Sulphur.
The family moved to Altus, Oklahoma where Allen worked as a schoolteacher. Loyce would care for his younger brother Lewis, born with Down’s syndrome. The pair became close. It must have broken Loyce’s heart when Lewis became and ill and died, while Loyce was still in Jr. High.
Loyce and his older brother Lance were busy during the High school years, caring for Grace following a debilitating stroke.
Loyce’s niece Bertha Deen Sullivan was little at the time, and still remembers. “Loyce was a tall dark handsome young man with deep blue eyes”. He would pick her up and ask “Who loves ya?”, and then he would kiss her on the forehead.
Altus was the kind of small town, where the newspaper printed the bio of every graduating High school senior. The Times-Democrat wrote that “Loyce Deen is a young man with high ambitions. He plans to enter the US Navy aeronautical mechanics division after graduation and finds subjects such as problems of American democracy, the most interesting. He has also been active in dramatics work at school.”
Loyce worked for a time with the government’s Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), and later joined the Douglas Aircraft Company in Wichita, building wing sets for the A-26 Invader attack bomber.
 Even before the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Loyce had wanted to join the Navy. In October 1942, he did just that. First there was basic training in San Diego, and then gunner’s school, learning all about the weapons systems aboard a Grumman TBF Avenger torpedo bomber. Then on to Naval Air School Fort Lauderdale, before joining the new 15th Air Group, forming out of Westerly, Rhode Island.
Even before the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Loyce had wanted to join the Navy. In October 1942, he did just that. First there was basic training in San Diego, and then gunner’s school, learning all about the weapons systems aboard a Grumman TBF Avenger torpedo bomber. Then on to Naval Air School Fort Lauderdale, before joining the new 15th Air Group, forming out of Westerly, Rhode Island.
On April 29, 1944, the Air Group reported for duty aboard the “Fightingest Ship in the Navy” at Pearl Harbor. The aircraft carrier, USS Essex.
An Air Group consists of eighty or so aircraft, of three distinct types. First are the fighters, the fast, single seat Grumman Hellcats. Next are the two-seat dive bombers, the Curtiss Helldivers, the pilot joined by a rear-seat gunner whose job it is to lay the one-ton bomb on the target, while handling a machine gun at the same time. Third is the torpedo bomber, the Grumman Avenger, with two enlisted crewmen in addition to the pilot. The Avenger carries a ton of bombs, depth charges or aerial torpedoes and, like the Helldiver, is designed for low-level attack.
 Loyce was the turret gunner on one of these Avengers, assigned to protect the aircraft from above and teamed up with Pilot Lt. Robert Cosgrove from New Orleans, Louisiana and Radioman Digby Denzek, from Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Loyce was the turret gunner on one of these Avengers, assigned to protect the aircraft from above and teamed up with Pilot Lt. Robert Cosgrove from New Orleans, Louisiana and Radioman Digby Denzek, from Grand Rapids, Michigan.
Cosgrove was a superb pilot, often returning aircraft to the carrier, so shot up as to seem unflyable. Digby had several jobs, including arming the weapons systems, and operating the radio. When the team was under fire, Digby would crawl down into a ball turret on the belly of the aircraft, his machine gun defending, from below.
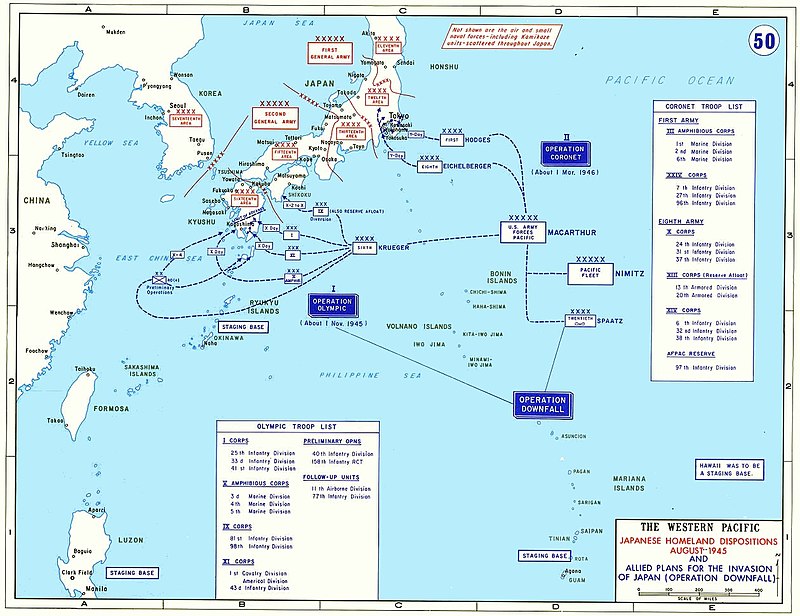
The 15th Air group saw some of the most intense fighting it had ever encountered during the battle of Leyte Gulf of October 24-25, 1944. Commander Lambert, who oversaw the Avenger squadron, described “Coming in through the most intense and accurate AA yet experienced, the squadron made three hits on one battleship, two hits on another battleship, and two hits each on two different heavy cruisers“.

Deen received a shrapnel wound to his foot sometime during the fighting of the 24th. He wrapped the thing up and stayed on to fight, the following day. He would receive a Purple heart medal for the wound. Posthumously.
Following rest and replenishment at Ulithi Atoll in the Caroline Islands, USS Essex was on station for the November 5 Battle of Manila Bay. Loyce could have stayed back on a hospital ship until that foot healed, but chose to ignore the injury and rejoin his unit.
Loyce’s niece Bertha, was not surprised. On being informed of his injury, she said “I’m not surprised he stayed with his unit. Loyce would not have it any other way – he would always remain at his post to make sure his brothers came home safely with him.”
Loyce Deen climbed into his gun turret for the last time on November 5. It was a two hour ride to the target zone in Manila Bay, with Japanese aircraft on the radar for most of that time, and the carriers USS Lexington and Ticonderoga, under kamikaze attack.
Lieutenant Cosgrove’s Avenger came under savage anti-aircraft fire, from a Japanese cruiser. Loyce Deen took two direct hits and was killed, instantly. The Avenger aircraft, tail number 93, was so smashed up as to be all but unflyable. It took all of the pilot’s strength and skill to fly the thing back through two thunderstorms, and land on the Essex.
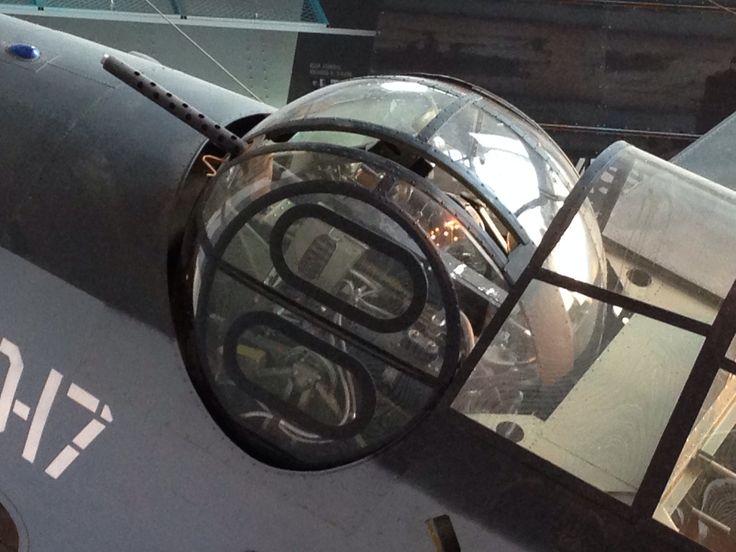

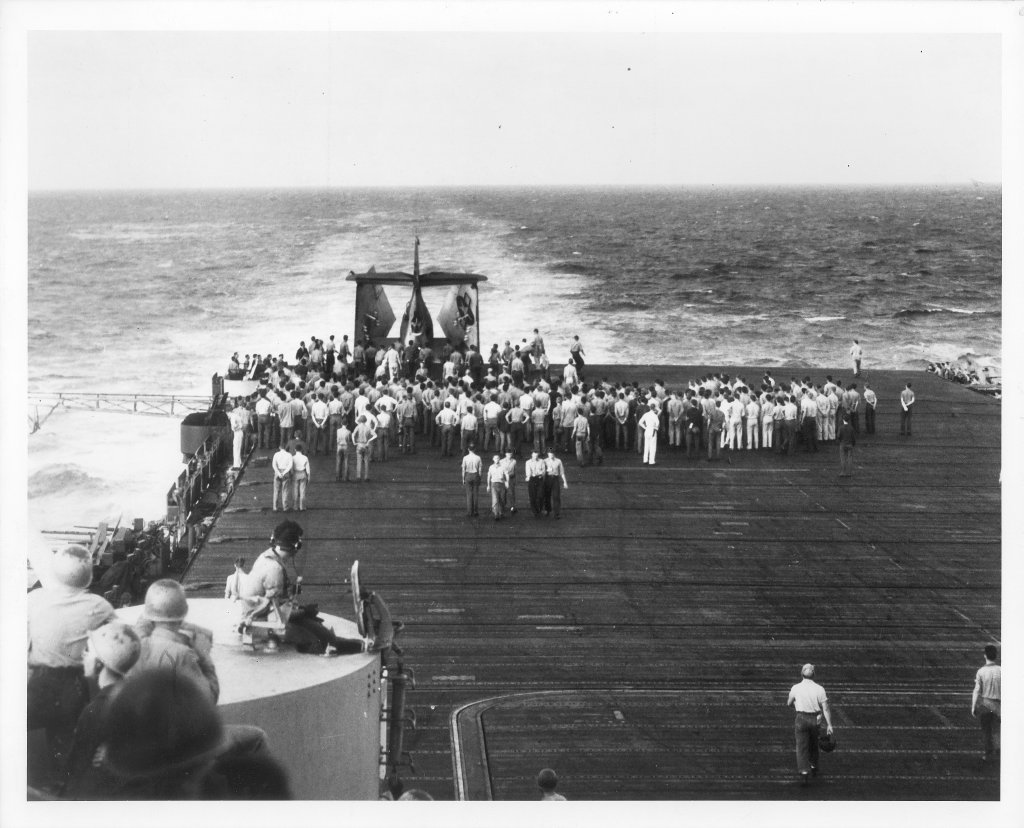
What remained of Loyce Edward Deen was so badly mangled, it was all but impossible to remove him from his smashed turret. For the first and last time in history, a man was deliberately buried at sea, inside of the aircraft he had served.
Fingerprints were taken and dog tags removed. This Avenger was not even scavenged, for parts. With the crew of the USS Essex assembled on deck, the shattered aircraft was pushed over the side. Two other Avengers flew overhead in salute, as the tail dipped beneath the waves.
Loyce Edward Deen, was going home.
Not long after the ceremony, the Essex went to General Quarters. There were kamikazes to deal with.
Lt. Cosgrove and the rest of Air Group 15 got back into their aircraft the following day and again on the 12th, 13th and 14th, and attacked those same cruisers in Manila Bay.
The Deen family would not receive the knock on the door, until Thanksgiving week.







 At first in no hurry to sign up, he even considered joining the French Army before returning home to England, to enlist in the Artists Rifles Training Corps, in October 1915.
At first in no hurry to sign up, he even considered joining the French Army before returning home to England, to enlist in the Artists Rifles Training Corps, in October 1915. After this experience, soldiers reported him behaving strangely. Owen was diagnosed as suffering from neurasthenia or shell shock, what we now understand to be Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, and sent to Craiglockhart War Hospital in Edinburgh, for treatment.
After this experience, soldiers reported him behaving strangely. Owen was diagnosed as suffering from neurasthenia or shell shock, what we now understand to be Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, and sent to Craiglockhart War Hospital in Edinburgh, for treatment. Owen continued to write through his period of convalescence, his fame as author and poet growing through the late months of 1917 and into March of the following year. Supporters requested non-combat postings on his behalf, but such requests were turned down. It’s unlikely he would have accepted them, anyway. His letters reveal a deep sense of obligation, an intention to return to the front to be part of and to tell the story of the common man, thrust by his government into uncommon conditions.
Owen continued to write through his period of convalescence, his fame as author and poet growing through the late months of 1917 and into March of the following year. Supporters requested non-combat postings on his behalf, but such requests were turned down. It’s unlikely he would have accepted them, anyway. His letters reveal a deep sense of obligation, an intention to return to the front to be part of and to tell the story of the common man, thrust by his government into uncommon conditions.

 Emil Joseph Kapaun was the son of Czech immigrants, a farm kid who grew up in 1920s Kansas. Graduating from Pilsen High, class of 1930, he spent much of the 30s in theological seminary, becoming an ordained priest of the Roman Catholic faith on June 9, 1940.
Emil Joseph Kapaun was the son of Czech immigrants, a farm kid who grew up in 1920s Kansas. Graduating from Pilsen High, class of 1930, he spent much of the 30s in theological seminary, becoming an ordained priest of the Roman Catholic faith on June 9, 1940. A single regiment was attacked by the 39th Chinese Corps on November 1, and completely overrun the following day. For the 8th Cav., the battle of Unsan was one of the most devastating defeats of the Korean War. Father Kapaun was ordered to evade, an order he defied. He was performing last rites for a dying soldier, when he was seized by Chinese communist forces.
A single regiment was attacked by the 39th Chinese Corps on November 1, and completely overrun the following day. For the 8th Cav., the battle of Unsan was one of the most devastating defeats of the Korean War. Father Kapaun was ordered to evade, an order he defied. He was performing last rites for a dying soldier, when he was seized by Chinese communist forces. Chinese Communist guards would taunt him during daily indoctrination sessions, “Where is your god now?” Before and after these sessions, he would move through the camp, ministering to Catholic and non-Catholic alike. Kapaun would slip in behind every work detail, cleaning latrines while other prisoners argued over who’d get the job. He’d wash the filthy laundry of those made weak and incontinent with dysentery.
Chinese Communist guards would taunt him during daily indoctrination sessions, “Where is your god now?” Before and after these sessions, he would move through the camp, ministering to Catholic and non-Catholic alike. Kapaun would slip in behind every work detail, cleaning latrines while other prisoners argued over who’d get the job. He’d wash the filthy laundry of those made weak and incontinent with dysentery. In the end, he was too weak to lift the plate that held the meager meal the guards left for him. US Army records report that he died of pneumonia on May 6, 1951, but his fellow prisoners will tell you that he died on May 23, of malnutrition and starvation. He was 35.
In the end, he was too weak to lift the plate that held the meager meal the guards left for him. US Army records report that he died of pneumonia on May 6, 1951, but his fellow prisoners will tell you that he died on May 23, of malnutrition and starvation. He was 35.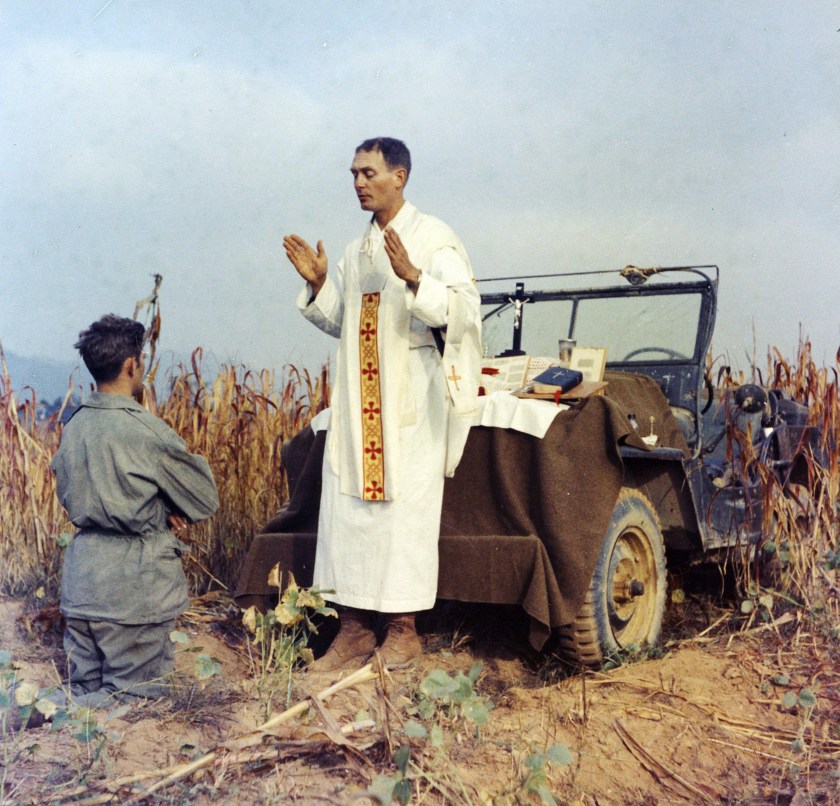





 Which brings us back to that funny-looking boat. The Office of Strategic Services (OSS), predecessor to the modern Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), built two of these semi-submersibles, code named “Gimik”, part of a top-secret operation code named “NAPKO”.
Which brings us back to that funny-looking boat. The Office of Strategic Services (OSS), predecessor to the modern Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), built two of these semi-submersibles, code named “Gimik”, part of a top-secret operation code named “NAPKO”.







 The radio drama began with a statement that, what followed, was fictional. The warning was repeated at the 40 and 55-minute mark, and again at the end of the broadcast. It began with a weather report, and then went to a dance band remote, featuring “Ramon Raquello and his orchestra”. The music was periodically interrupted by live “news” flashes, beginning with strange explosions on Mars. Producer Orson Welles made his first radio appearance as the “famous” (but non-existent) Princeton Professor Dr. Richard Pierson, who dismissed speculation about life on Mars.
The radio drama began with a statement that, what followed, was fictional. The warning was repeated at the 40 and 55-minute mark, and again at the end of the broadcast. It began with a weather report, and then went to a dance band remote, featuring “Ramon Raquello and his orchestra”. The music was periodically interrupted by live “news” flashes, beginning with strange explosions on Mars. Producer Orson Welles made his first radio appearance as the “famous” (but non-existent) Princeton Professor Dr. Richard Pierson, who dismissed speculation about life on Mars. A short time later, another “news flash” reported a fiery crash in Grovers Mill, NJ. What was originally thought to be a meteorite was revealed to be a rocket machine as a tentacled, pulsating Martian unscrewed the hatch and incinerated the crowd with a death ray.
A short time later, another “news flash” reported a fiery crash in Grovers Mill, NJ. What was originally thought to be a meteorite was revealed to be a rocket machine as a tentacled, pulsating Martian unscrewed the hatch and incinerated the crowd with a death ray.
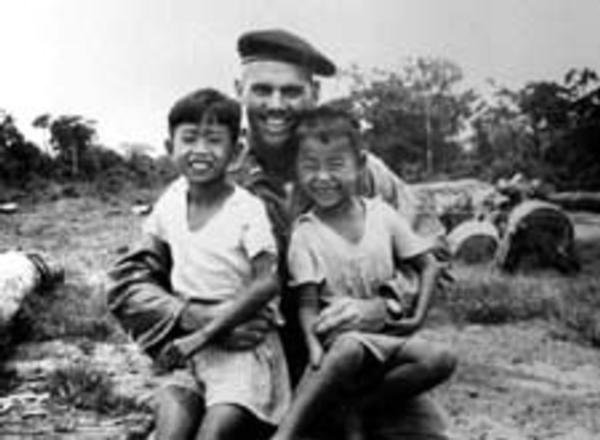


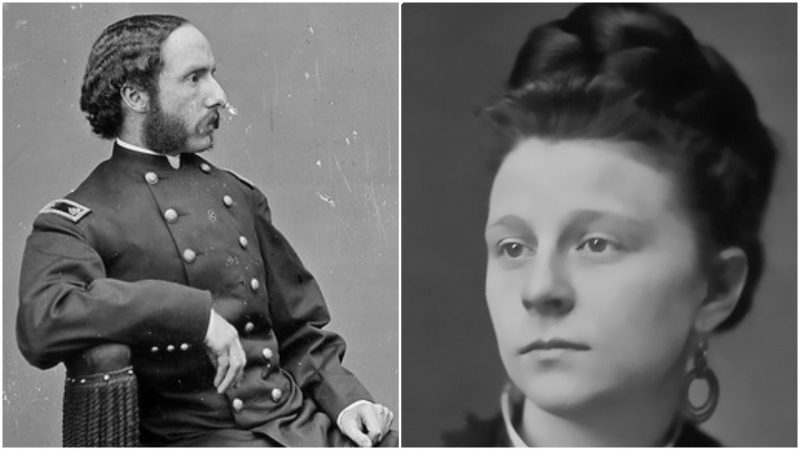
 Humbert Roque Versace was born in Honolulu on July 2, 1937, the oldest of five sons born to Colonel Humbert Joseph Versace. Writer Marie Teresa “Tere” Rios was his mother, author of the
Humbert Roque Versace was born in Honolulu on July 2, 1937, the oldest of five sons born to Colonel Humbert Joseph Versace. Writer Marie Teresa “Tere” Rios was his mother, author of the  He did his tour, and voluntarily signed up for another six months. By the end of October 1963, Rocky had fewer than two weeks to the end of his service. He had served a year and one-half in the Republic of Vietnam. Now he planned to go to seminary school. He had already received his acceptance letter, from the Maryknoll order.
He did his tour, and voluntarily signed up for another six months. By the end of October 1963, Rocky had fewer than two weeks to the end of his service. He had served a year and one-half in the Republic of Vietnam. Now he planned to go to seminary school. He had already received his acceptance letter, from the Maryknoll order.


 The effect was entirely unacceptable to his Communist tormentors. To the people of these villages, this man made sense.
The effect was entirely unacceptable to his Communist tormentors. To the people of these villages, this man made sense.

 South Carolina seceded in December 1860, and the world waited to see who’d follow. New York City became the next to call for secession on January 6, when Mayor Fernando Wood addressed the city’s governing body. “When Disunion has become a fixed and certain fact”, he said, “why may not New York disrupt the bands which bind her to a venal and corrupt master…and destroyed the Confederacy of which she was the proud Empire City?”
South Carolina seceded in December 1860, and the world waited to see who’d follow. New York City became the next to call for secession on January 6, when Mayor Fernando Wood addressed the city’s governing body. “When Disunion has become a fixed and certain fact”, he said, “why may not New York disrupt the bands which bind her to a venal and corrupt master…and destroyed the Confederacy of which she was the proud Empire City?”

 A courier express note arrived on October 7, 1945. “There are few controversies that are not susceptible to a peace time resolution” read the note, “if examined in an atmosphere of tranquility and calm rather than strife and turmoil. I would suggest the possibility of roast veal as a vehicle of peace. Why don’t you run down the fattest calf in Erie County, barbecue it and serve it with fixin’s in the old blacksmith shop where the ruckus started? Who can tell? The dissidents might decide to resume citizenship.” The note was signed “Very Sincerely Yours, Harry Truman”.
A courier express note arrived on October 7, 1945. “There are few controversies that are not susceptible to a peace time resolution” read the note, “if examined in an atmosphere of tranquility and calm rather than strife and turmoil. I would suggest the possibility of roast veal as a vehicle of peace. Why don’t you run down the fattest calf in Erie County, barbecue it and serve it with fixin’s in the old blacksmith shop where the ruckus started? Who can tell? The dissidents might decide to resume citizenship.” The note was signed “Very Sincerely Yours, Harry Truman”.![4b4cf0f864c3dabcdb_IMG_7326[1]](https://todayinhistory.blog/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/4b4cf0f864c3dabcdb_img_73261.jpg?w=684&h=513)

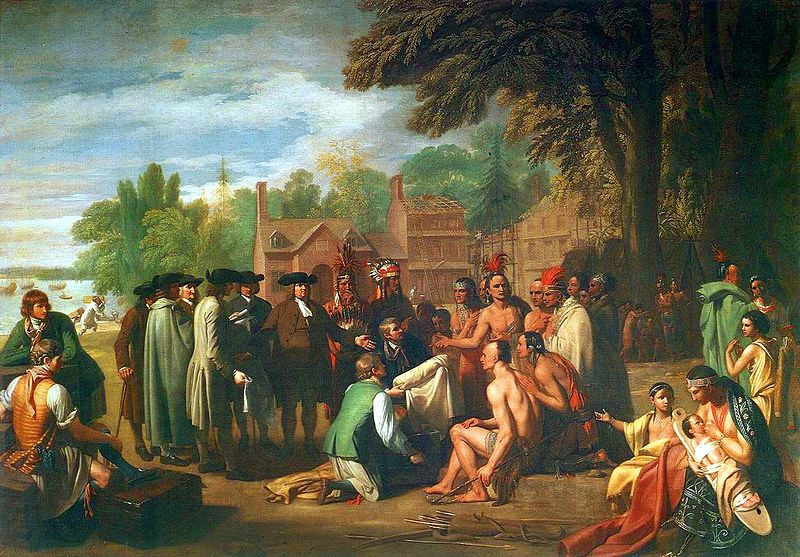
 Tammany Societies adopted a number of native terms, with leaders calling themselves Grand Sachem, and meeting in halls called “Wigwams”. The most famous of these was incorporated in New York on May 12, 1789.
Tammany Societies adopted a number of native terms, with leaders calling themselves Grand Sachem, and meeting in halls called “Wigwams”. The most famous of these was incorporated in New York on May 12, 1789.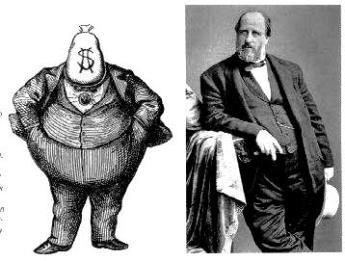
 Some among the self-styled “Uppertens”, the top 10,000 amid New York’s socioeconomic strata, fell in with the self-dealing and corruption of the Tammany Hall machine. Others counted on an endless supply of cheap immigrant labor.
Some among the self-styled “Uppertens”, the top 10,000 amid New York’s socioeconomic strata, fell in with the self-dealing and corruption of the Tammany Hall machine. Others counted on an endless supply of cheap immigrant labor.
 Next is the spoils system, itself. To this day, too many think it’s government’s job to “Bring home the Bacon”, not seeming to realize that they are themselves, the hogs. The Roosevelt administrations’ efforts to fix the Great Depression resulted in a blizzard of bacon from an increasingly Nationalized federal government, separating the local machines from their proximate base of support.
Next is the spoils system, itself. To this day, too many think it’s government’s job to “Bring home the Bacon”, not seeming to realize that they are themselves, the hogs. The Roosevelt administrations’ efforts to fix the Great Depression resulted in a blizzard of bacon from an increasingly Nationalized federal government, separating the local machines from their proximate base of support.
You must be logged in to post a comment.