The French battle fleet lay at anchor in late 1942, France itself under German occupation. Defeated but unbeaten, the French sailors of “La Royale” weren’t about to hand it all over to the Nazis. Even if they had to destroy it with their own hands.

The Battle of France began on May 10, 1940, with the German invasion of France and the low countries of Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Barely three weeks later, the shattered remnants of the allied armies crowded the beaches and jetties of Dunkirk, awaiting evacuation.
The speed and ferocity of the German Blitzkrieg left the French people in shock. All those years their government had told them. The strength of the French army combined with the Maginot line was more than enough to counter German aggression.
France had fallen in six weeks.
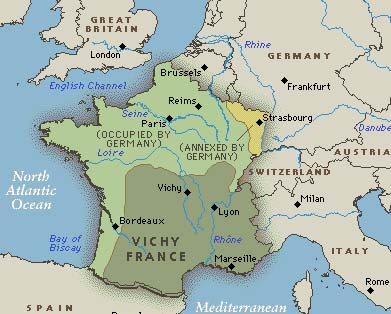
Germany installed a Nazi-approved French government in the south of the country, headed by WW1 hero Henri Pétain. Though mostly toothless, the self-described “French state” in Vichy was left relatively free to run its own affairs compared with the Nazi occupied regions to the west and north.
That all changed in November 1942, with the joint British/American invasion of North Africa. At the time, Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria were nominally under the control of the Vichy regime. Hitler gave orders for the immediate occupation of all France.
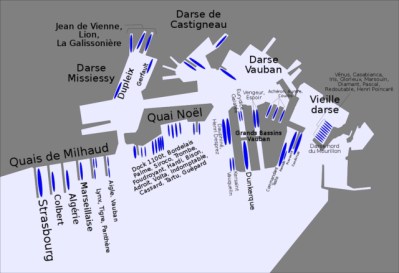
With the armistice of June 1940, much of the French naval fleet was confined to the Mediterranean port of Toulon. Confined but not disarmed, and the French fleet possessed some of the most advanced naval technologies of the age, enough to shift the balance of military power in the Mediterranean.
While many considered the Vichy government to be a puppet state, the officers and men of the French fleet had no love for their German occupiers. This was a French fleet and would remain so if they could help it. Even if they had to destroy it by their own hands.

In November 1942, the Nazi government came to take control of that fleet. The motorized 7th Panzer column of German tanks, armored cars and armored personnel carriers descended on Toulon with an SS motorcycle battalion, taking over port defenses to either side of the harbor. German officers entered fleet headquarters and arrested French officers, but not before word of what was happening reached French Admiral Jean de Laborde, aboard the flagship Strasbourg.
The order went out across the base at Toulon. Prepare to scuttle the fleet and resist the advance of German troops. By any means necessary.

The German column approached the main gate to the harbor facility in the small hours of November 27, demanding access. ‘Of course,’ smiled the French guard. ‘Do you have your access paperwork?’

Under orders to take the harbor without bloodshed, the Nazi commander was dismayed. Was he being denied access by this, his defeated adversary? Minutes seemed like hours in the tense wrangling that followed. Germans gesticulated and argued with French guards who stalled and prevaricated at the closed gate.
The Germans produced documentation, only to be politely thanked, asked to wait, and left standing at the gate.
Meanwhile, thousands of French seamen worked in grim silence throughout the early morning hours, preparing to scuttle their own fleet. Valves and watertight doors were opened, incendiary and demolition charges were prepared and placed.

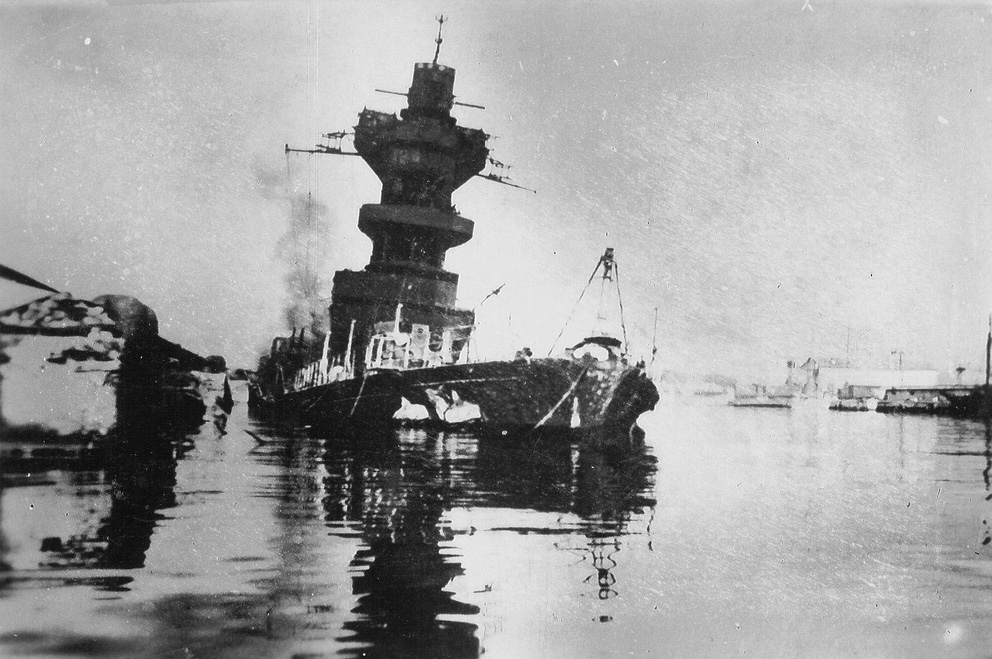
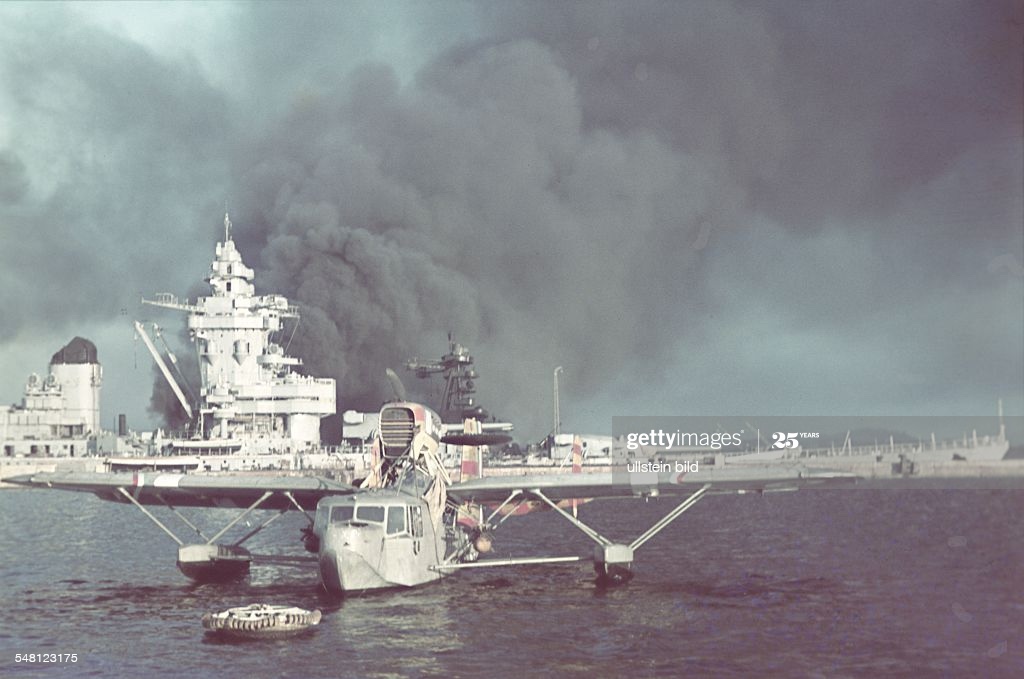
Finally, the Panzer column could be stalled no more. German tanks rumbled through the main gate at 5:25am, even as the order to scuttle passed throughout the fleet. Dull explosions sounded across the harbor. Fighting broke out by the early dawn light between the German column and French sailors pouring out of their ships. Lead German tanks broke for the Strasbourg, even now pouring greasy, black smoke from her superstructure as she settled to the bottom.
The Germans could only look on helpless, as a dying fleet escaped their grasp. In the end, 3 battleships, 7 cruisers, 15 destroyers, 13 torpedo boats, 6 sloops, 12 submarines, 9 patrol boats, 19 auxiliary ships, 28 tugs, 4 cranes and a school ship were destroyed. 39 smaller vessels of negligible military value fell into German hands along with twelve fleet vessels, all of them damaged.
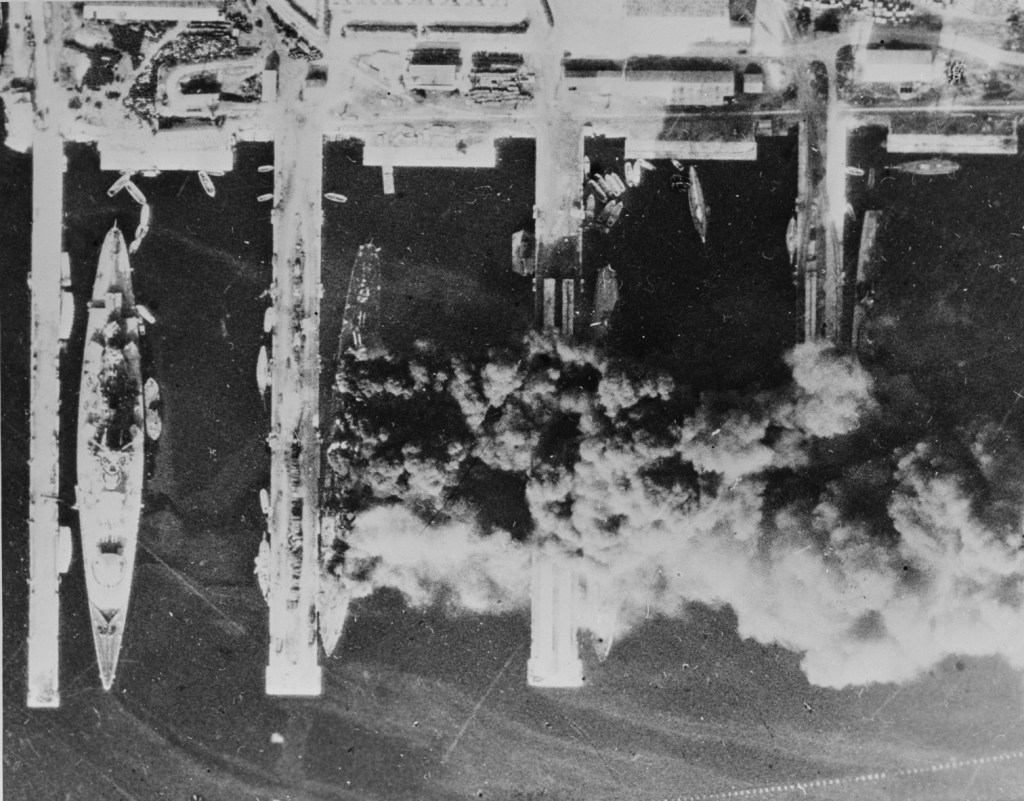
The fires burned on for weeks. The harbor at Toulon remained fouled and polluted for years.
The French Navy lost 12 men killed and 26 wounded that day, 82 years ago, today. The loss to the Nazi war effort is incalculable. How many lives may have been lost had Nazi Germany come into possession of all that naval power. But for the obstinate bravery of a vanquished, but still unbeaten foe.




You must be logged in to post a comment.