The international slave trade was illegal in most countries by 1839 while the “peculiar institution” of slavery remained legal. In April of that year, a Portuguese slave trader illegally purchased some 500 Africans and shipped them to Havana aboard the slave ship Teçora.
Conditions were so horrific aboard Teçora that fully one-third of its “cargo”, presumably healthy individuals, died on the journey. Once in Cuba, sugar cane producers Joseph Ruiz and Pedro Montez purchased 49 members of the Mende people, 49 adults and four children, for use on the plantation.
The Mendians were given Spanish names and designated “black ladinos,” fraudulently documenting the 53 to have always lived as slaves in Cuba. In June of 1841 Ruiz and Montez placed the Africans on board the schooner la Amistad, (“Friendship”), and set sail down the Cuban coast to Puerto del Principe.

Africans had been chained onboard Teçora but chains were judged unnecessary for the short coastal trip aboard Amistad. On the second day at sea, two Mendians were whipped for an unauthorized trip to the water cask. One of them asked where they were being taken. The ship’s cook responded, they were to be killed and eaten.
The cook’s mocking response would cost him his life.
That night, captives armed with cane knives seized control of the ship. Their leader was Sengbe Pieh, also known as Joseph Cinqué. Africans killed the ship’s Captain and the cook losing two of their own in the struggle. Montez was seriously injured while Ruiz and a cabin boy named Antonio, were captured and bound. The rest of the crew escaped in a boat.
The mulatto cabin boy who really was a black ladino, would be used as translator.
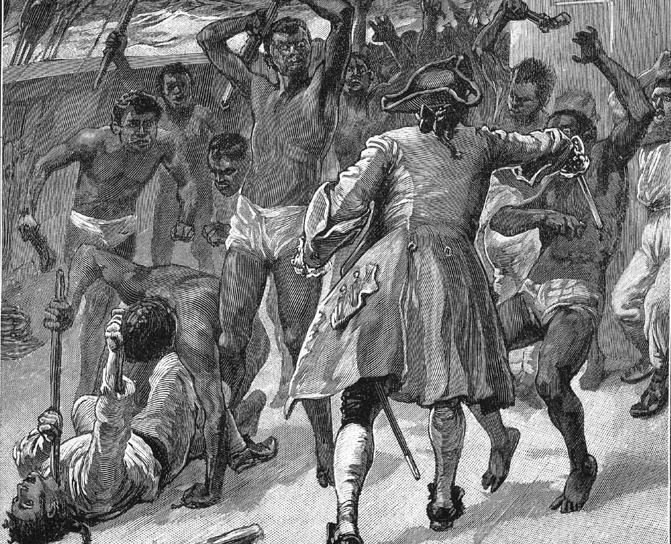

Mendians forced the two to return them to their homeland, but the Africans were betrayed. By day the two would steer east, toward the African coast. By night when the position of the sun could not be determined, the pair would turn north. Toward the United States.
After 60 days at sea, Amistad came aground off Montauk on Long Island Sound. Several Africans came ashore for water when Amistad was apprehended by the US Coastal Survey brig Washington, under the command of Thomas Gedney and Richard Meade. Meanwhile on shore, Henry Green and Pelatiah Fordham (the two having nothing to do with the Washington) captured the Africans who had come ashore.

Amistad was piloted to New London Connecticut, still a slave state at that time. The Mendians were placed under the custody of United States marshals.
Both the slave trade and slavery itself were legal at this time according to Spanish law while the former was illegal in the United States. The Spanish Ambassador demanded the return of Ruiz’ and Montez’ “property”, asserting the matter should be settled under Spanish law. American President Martin van Buren agreed, but, by that time, the matter had fallen under court jurisdiction.
Gedney and Meade of the Washington sued under salvage laws for a portion of the Amistad’s cargo, as did Green and Fordham. Ruiz and Montez sued separately. The district court trial in Hartford determined the Mendians’ papers to be forged. These were now former slaves entitled to be returned to Africa.
Antonio was ruled to have been a slave all along and ordered returned to Cuba. He fled to New York with the help of white abolitionists and lived out the rest of his days as a free man.
Fearing the loss of pro-slavery political support, President van Buren ordered government lawyers to appeal the case up to the United States Supreme Court. The government’s case depended on the anti-piracy provision of a treaty then in effect between the United States, and Spain.
A former President, son of a Founding Father and eloquent opponent of ‘peculiar institution’ John Quincy Adams argued the case in a trial beginning on George Washington’s birthday, 1841.

In United States v. Schooner Amistad, the Supreme Court upheld the decision of the lower court 8-1, ruling that the Africans had been detained illegally and ordering them returned to their homeland.
Pro slavery Whig John Tyler was President by this time, refusing to provide a ship or to fund the repatriation. Abolitionists and Christian missionaries stepped in, 34 surviving Mendians departing for Sierra Leone on November 25, 1841 aboard the ship, Gentleman.
The Amistad story has been told in books and in movies and is familiar to many. One name perhaps not so familiar is that of James Benjamin Covey. James Covey was born Kaweli sometime around 1825, in what is now the the border region between of Sierra Leone, Guinea and Liberia. Kidnapped in 1833 and taken aboard the Segundo Socorro, Kaweli was an illegal slave when the vessel was seized by the Royal Navy.
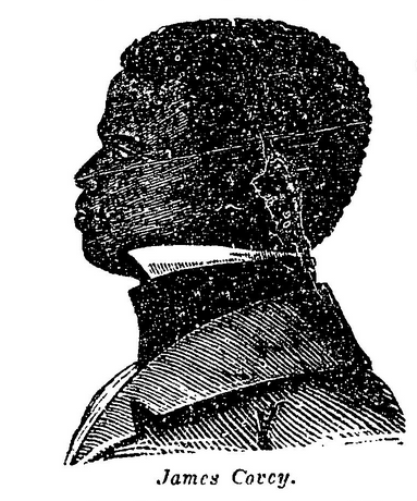

Kaweli went to school for five years in Bathurst, Sierra Leone, where he took the name of James Benjamin Covey. Joining the Royal Navy, Covey participated in the capture of several illegal slave ships.
Hired on as live interpreter, James Covey was to play a crucial role in the Medians’ trial before the Supreme Court. He would also accompany the 34 on their return to the African continent.
James Covey, aka Kaweli, was going home.
‘They all have Mendi names and their names all mean something… They speak of rivers which I know. They sailed from Lomboko… two or three speak different language from the others, the Timone language… They all agree on where they sailed from. I have no doubt they are Africans.’ – James Benjamin Covey
Gentleman landed in Sierra Leone in January 1842, where some of the Africans helped establish a Christian mission. Most including Joseph Cinque himself returned to homelands in the African interior. One survivor, a little girl when it all started by the name of Margru, returned to the United States where she studied at Ohio’s integrated Oberlin College, returning to Sierra Leone as the Christian missionary Sara Margru Kinson.

In arguing the case, President Adams took the position that no man, woman or child in the United States could ever be sure of the “blessing of freedom” if the President could hand over free men on the demand of a foreign government.
A century and a half later later President Bill Clinton, Deputy Attorney General Eric Holder and AG Janet Reno orchestrated the kidnap of six-year-old Elián González at gunpoint, returning him to Cuba over the body of the mother who had drowned bringing her boy to freedom.



 2,500 years ago, Bantu farmers on the African continent began to spread out across the land as the first Africans penetrated the dense rain forests of the equator, to take up a new life on the west African coast.
2,500 years ago, Bantu farmers on the African continent began to spread out across the land as the first Africans penetrated the dense rain forests of the equator, to take up a new life on the west African coast.
 Home to one of the few safe harbors on the surf-battered “windward coast”, Sierra Leone soon became a favorite of European mariners, some of whom remained for a time while others came to stay, intermarrying with local women.
Home to one of the few safe harbors on the surf-battered “windward coast”, Sierra Leone soon became a favorite of European mariners, some of whom remained for a time while others came to stay, intermarrying with local women. While this type of “slave” retained rudimentary rights at this time, those unfortunate enough to be captured by Dutch, English and French slavers, did not.
While this type of “slave” retained rudimentary rights at this time, those unfortunate enough to be captured by Dutch, English and French slavers, did not.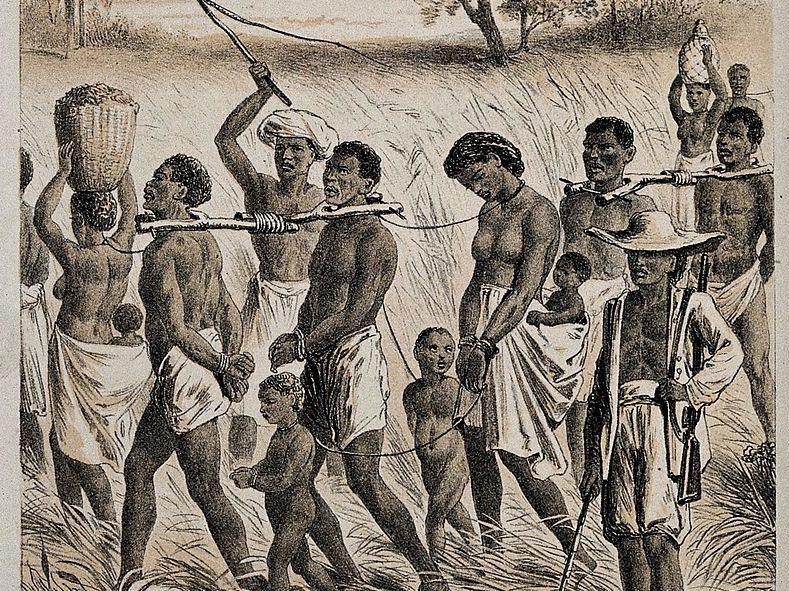 This was the world of John Newton, born July 24 (old style) 1725 and destined to a life, in the slave trade.
This was the world of John Newton, born July 24 (old style) 1725 and destined to a life, in the slave trade.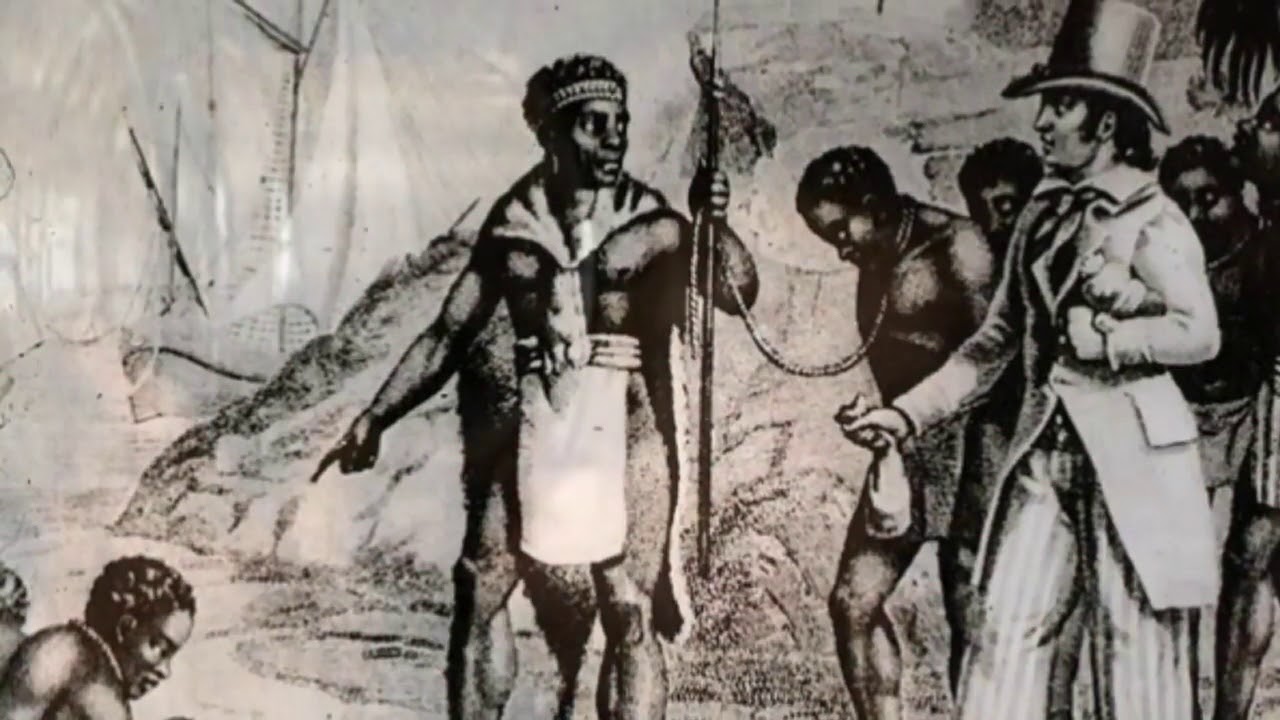 Newton hated life on the Pegasus as much as they, hated him. In 1745, they left him in West Africa with slave trader Amos Clowe. Newton was now himself a slave, given by Clowe to his wife Princess Peye of the Sherbro tribe. Peye treated Newton as horribly as any of her other slaves. Newton himself later described these three years as “once an infidel and a libertine, [now] a servant of slaves in West Africa”.
Newton hated life on the Pegasus as much as they, hated him. In 1745, they left him in West Africa with slave trader Amos Clowe. Newton was now himself a slave, given by Clowe to his wife Princess Peye of the Sherbro tribe. Peye treated Newton as horribly as any of her other slaves. Newton himself later described these three years as “once an infidel and a libertine, [now] a servant of slaves in West Africa”.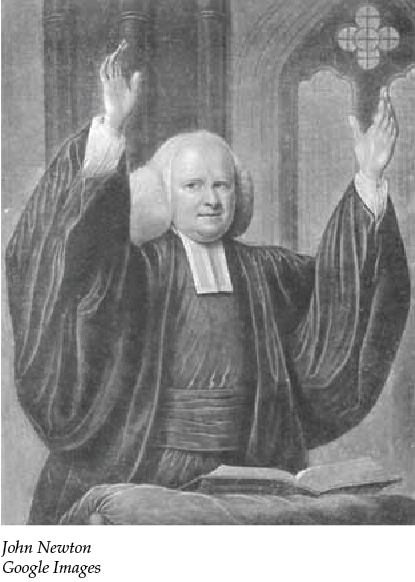 Moving to London in 1780 as the Rector of St. Mary Woolnoth church, Newton became involved with the Committee for the Abolition of the Slave Trade.
Moving to London in 1780 as the Rector of St. Mary Woolnoth church, Newton became involved with the Committee for the Abolition of the Slave Trade. William Cowper was an English poet and hymnist who came to worship in Newton’s church, in 1767. The pair collaborated on a book of Newton’s hymns including “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken,” “How Sweet the Name of Jesus Sounds!,” “Come, My Soul, Thy Suit Prepare” and others.
William Cowper was an English poet and hymnist who came to worship in Newton’s church, in 1767. The pair collaborated on a book of Newton’s hymns including “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken,” “How Sweet the Name of Jesus Sounds!,” “Come, My Soul, Thy Suit Prepare” and others.
You must be logged in to post a comment.